Boston Scientific accounts are for healthcare professionals only.

EKOS™ Endovascular System
Reimbursement
Configure or select a product to continue to order
- Overview
- Ultrasonic technology
- Technical specifications
- Ordering information
- Clinical evidence
- Training
- Resources
EKOS features & benefits
EKOS is a safe, repeatable and reliable treatment that dissolves thrombus quickly with low lytic, low blood loss and low trauma – resulting in proven long-term outcomes. EKOS leverages the power of targeted ultrasonic waves to thin and separate fibrin strands and accelerates lytic dispersion deeper into the clot. The addition of the new EKOS+ catheter offers the same procedure & clinical workflow, with 50% more ultrasound power.1
Ultrasonic core technology
- Minimally invasive, 15-minute EKOS procedure that is quick to perform
- Lytic agent: as low as 8 mg tPA used2
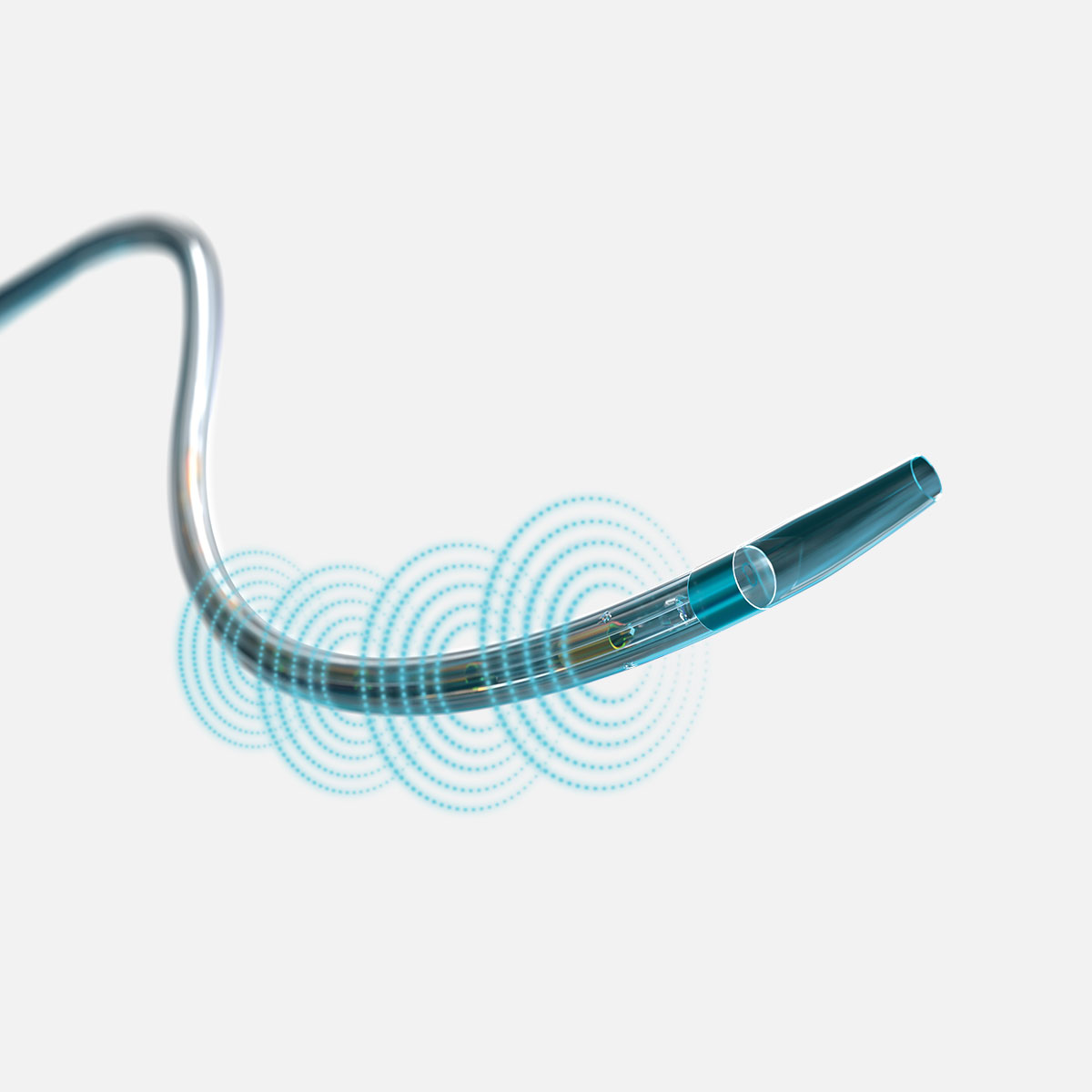
- Ultrasonic waves accelerate clot dissolution by unwinding and thinning fibrin strands to expose more drug receptor sites; acoustic streaming drives the drug deeper into the clot for safe dissolution

Target thrombus safety
Superior clot dissolution
Acoustic pulse acceleration
EKOS+ Endovascular System: How it works
- Bench data on File
- Tapson V et al. A randomized trial of the optimum duration of acoustic pulse thrombolysis procedure in acute intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions 2018; 11(14):1401-1410.
The EKOS ultrasound difference
EKOS is a minimally invasive system for dissolving thrombus. The ultrasonic core generates an acoustic field which greatly accelerates lytic dispersion by driving the drug deeper into the clot and unwinding the fibrin to expose plasminogen receptor sites.
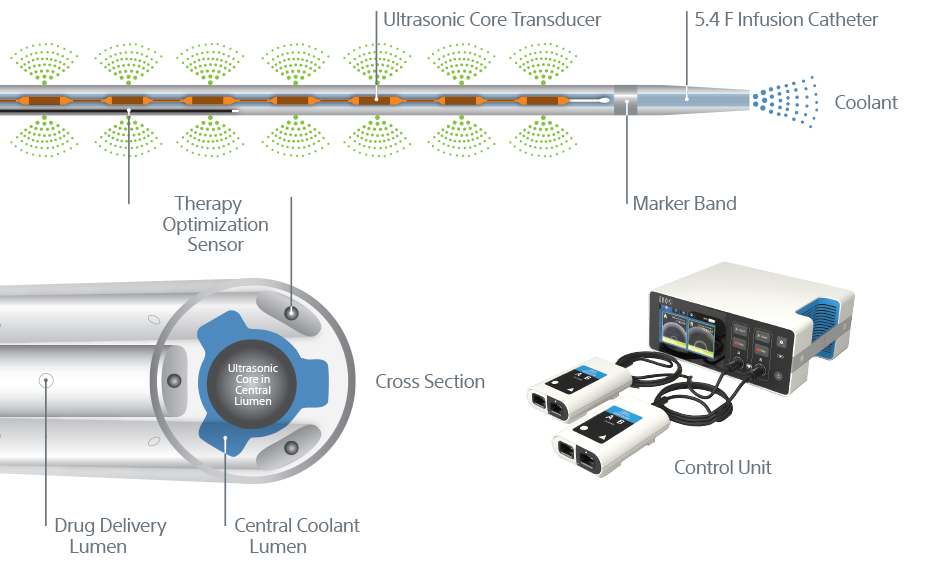
EKOS' targeted ultrasound waves accelerate thrombus dissolution by unwinding the fibrin matrix.1
1. Braaten JV et al. Ultrasound reversibly disaggregates fibrin fibers.Thromb Haemost 1997;78:1063-8
Technical information
EKOS™ Endovascular System
- 5.4 F infusion catheter for all EKOS products
- 106 cm infusion catheter (.035” guidewire compatible) with one ultrasonic core matched to corresponding length
- Treatment zones from 6 cm – 50 cm
- 135 cm infusion catheter (.035” guidewire compatible) with one ultrasonic core matched to corresponding length
- Treatment zones from 12 cm – 50 cm
EKOS™+ Endovascular System
- 7.8 F infusion catheter for all EKOS+ products
- 106 cm infusion catheter (0.035" guidewire compatible) with one ultrasonic core matched to corresponding length
- Treatment zones from 8 cm – 20 cm
- 135 cm infusion catheter (0.035" guidewire compatible) with one ultrasonic core matched to corresponding length
- Treatment zones from 8 cm – 20 cm
See Ordering Information for additional details
Now available: EKOS Control Unit 4.0
EKOS Control Unit 4.0 (EKOS CU4.0) offers new functionality and workflow-based intelligence for EKOS devices both at the procedure table and in the ICU. It is a critical part of the EKOS system that continues to break new ground in the treatment of PE.
EKOS CU4.0 is the result of extensive collaboration with our clinician partners to improve every step of the EKOS therapy experience to support your team's ability to perform at its highest level making workflow easier and more integrated from the lab to ICU. New features of the EKOS CU4.0 include an interactive color touchscreen, a built-in battery and separate ports for managing two EKOS devices simultaneously, simplifying bilateral treatment of pulmonary embolism (PE).
EKOS control Unit 4.0 console overview
Bilateral PE treatment, simplified
- Manages two EKOS Devices at once with A/B channels and easy-to-read screens for bilateral PE Acoustic Pulse Thrombolysis treatment.
- Small, lightweight and portable allowing easy integration into hospital workflow.
- Speeds set-up time with easy to follow on-screen step-by-step prompts.
- Intelligent on-screen troubleshooting tells you where the issue is and how to correct it.
- Built in battery makes it easier to transport patients from the lab with zero interruption in therapy.
Compatibility
- EKOS CU4.0 will run all EKOS devices currently run by the PT-3B Control Unit.
- EKOS+ is only compatible with the Control Unit 4.0.
Ordering information
EKOS™ Endovascular System
5.4 F infusion catheter for all EKOS products.
106 cm infusion catheter (0.035" guidewire compatible) with one ultrasonic core matched to corresponding length.
UPN/Order code | GTIN | Catheter length (cm) | Treatment zone (cm) |
500-55106 | 858593006028 | 106 | 6 |
500-55112 | 858593006134 | 106 | 12 |
500-55118 | 858593006141 | 106 | 18 |
500-55124 | 858593006158 | 106 | 24 |
500-55130 | 858593006165 | 106 | 30 |
500-55140 | 858593006172 | 106 | 40 |
500-55150 | 858593006189 | 106 | 50 |
135 cm infusion catheter (0.035" guidewire compatible) with one ultrasonic core matched to corresponding length.
UPN/Order code | GTIN | Catheter length (cm) | Treatment zone (cm) |
500-56112 | 858593006264 | 135 | 12 |
500-56130 | 858593006295 | 135 | 30 |
500-56140 | 858593006301 | 135 | 40 |
500-56150 | 858593006318 | 135 | 50 |
EKOS™+ Endovascular System
7.8 F infusion catheter for all EKOS+ products.
106 cm infusion catheter (0.035" guidewire compatible) with one ultrasonic core matched to corresponding length.
UPN/Order code | GTIN | Catheter length (cm) | Treatment zone (cm) |
H74939605106080 | 191506015459 | 106 | 8 |
H74939605106120 | 191506015466 | 106 | 12 |
H74939605106160 | 191506015473 | 106 | 16 |
H74939605106200 | 191506015480 | 106 | 20 |
135 cm infusion catheter (0.035" guidewire compatible) with one ultrasonic core matched to corresponding length.
UPN/Order code | GTIN | Catheter length (cm) | Treatment zone (cm) |
H74939605135080 | 191506015497 | 135 | 8 |
H74939605135120 | 191506015503 | 135 | 12 |
H74939605135160 | 191506015510 | 135 | 16 |
H74939605135200 | 191506015527 | 135 | 20 |
EKOS™ Endovascular System Control Unit 4.0
UPN / Order code | GTIN | Equipment class | Power requirements | Size | Weight |
600-40500 | 858593006462 | Class II (product code KRA) | 250VAC, 50/60Hz | 26.9 x 22.7 x 11.4 cm | 12.5 lb |
EKOS clinical trials and highlights
EKOS offers a safe and effective treatment to dissolve thrombus in the body's vascular system. With Level 1, Long-Term, and Quality of Life data, EKOS is the most studied device in the space.
EKOS uses targeted ultrasonic waves in combination with clot-dissolving drugs in the treatment of PE. Clinical evidence shows the therapy's ability to effectively target an entire clot without an increase in bleeding complications.
Efficacy
EKOS has been shown to yield safe and effective results for acute, massive and submassive PE.
- Reduces RV/LV ratio by more than 23% on average in as little as 2 hours
- Reduces PA pressures by 28% (at 48 hours)
- Up to 88-92% less thrombolytic dose than standard systemic treatment 1,2
- Minimized risk of bleeding
| Study | RV/LV reduction |
| ULTIMA | 23% (24 hours) |
| SEATTLE II | 25% (48 hours) |
| OPTALYSE | 23-26% (48 hours) |
Safety
EKOS has been shown to have a low risk of bleeding and ICH.
- Low major bleeding rate across studies (1.44%)
- ICH rate of 0.4% across major studies, two with 0 instances of ICH
| Study | Safety | Total dose |
| ULTIMA | 0% (Major bleed) | 0 (ICH) | 20mg |
| SEATTLE II | 0.67% (Severe bleed) | 0 (ICH) | 24mg |
| OPTALYSE | 3% (Major bleed) | 1 (ICH) | 4/8mg-12/24mg |
| Study name | Study description (Level) | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Venous thromboembolism: Deep venous thrombosis* | ||
| CAVA | A randomised controlled multicenter trial comparing ultrasound-accelerated catheter-directed thrombolysis, combined with standard anticoagulant therapy, with standard anticoagulant therapy alone, for acute primary iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis (Level 1) | Enrolling |
| ACCESS PTS | Accelerated thrombolysis for post-thrombotic syndrome using the EKOS system (Level 2) Download the data summary | Completed |
| Venous thromboembolism: Pulmonary embolism | ||
| ULTIMA | Ultrasound accelerated thrombolysIs of pulmonary embolism (Level 1) | Completed |
| SEATTLE II | A prospective, single-arm, multi-center trial of EKOS for acute pulmonary embolism (Level 2) | Completed |
| OPTALYSE PE | Study of the optimum duration of acoustic pulse thrombolysis procedure in the treatment of acute submassive pulmonary embolism (Level 2) | Completed |
| KNOCOUT PE | International EKOS registry of the treatment and clinical outcomes of patients with pulmonary embolism | Completed |
| Arterial occlusion* | ||
| DUET | Dutch randomized trial comparing standard catheter-directed thrombolysis versus ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis for thrombo-emoblic infra-inguinal | Completed |
| DUET II | Dutch randomized trial comparing standard catheter-directed thrombolysis versus ultrasound-accelerated thrombolysis for thrombo-emoblic infra-inguinal | Start-up |
*Safety and effectiveness have not been established in this patient population
1. Tapson V et al. A randomized trial of the optimum duration of acoustic pulse thrombolysis procedure in acute intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. JACC:Cardiovascular Interventions 2018; 11(14):1401-1410.
2. Konstantinides S, Geibel A, Heusel G, et al. Heparin plus alteplase compared with heparin alone in patients with submassive pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med.2002;347:1143–1150.
Training for the EKOS Endovascular System
Online medical training and education courses
The EDUCARE online platform makes healthcare education and training more relevant, more comprehensive, more personal, and more accessible. Register to access a library of procedural videos, case studies, training resources, and events.

