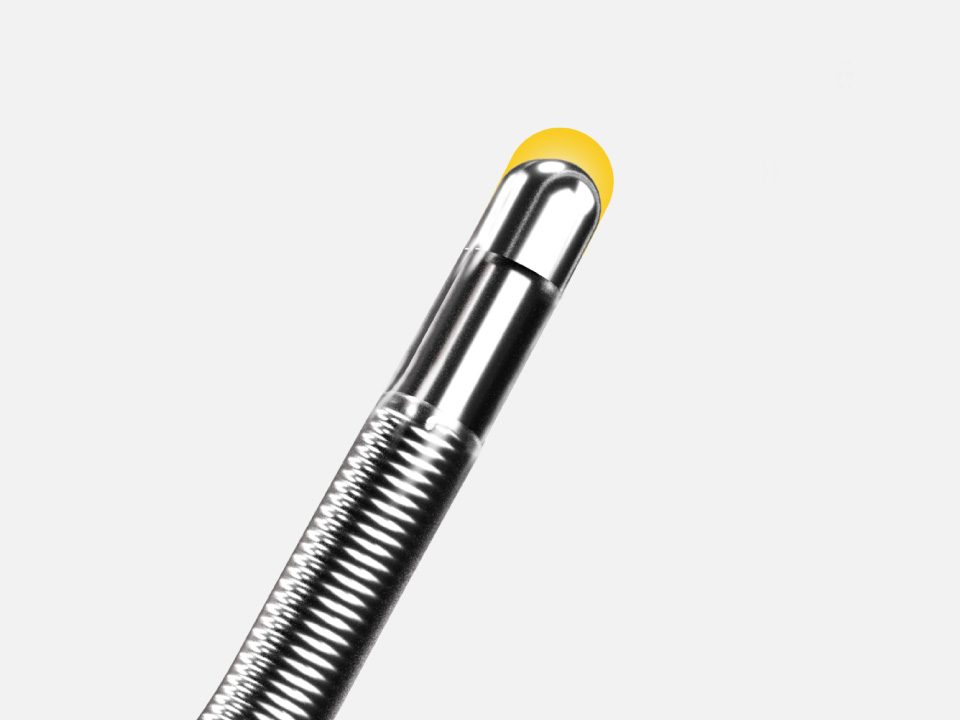
SupraCross™ RF Transseptal Solution
The SupraCross RF Transseptal Solution enables transseptal access using an alternate approach with the SupraCross Steerable Sheath and SupraCross RF Wire.
Configure or select a product to continue to order
- Overview
- Clinical data
- Technical specifications
- Ordering information
- Training
- Resources
Left atrial access from any approach™
When the conventional solution may not be optimal, use the SupraCross RF Transseptal Solution to gain alternate access into the left atrium (LA)
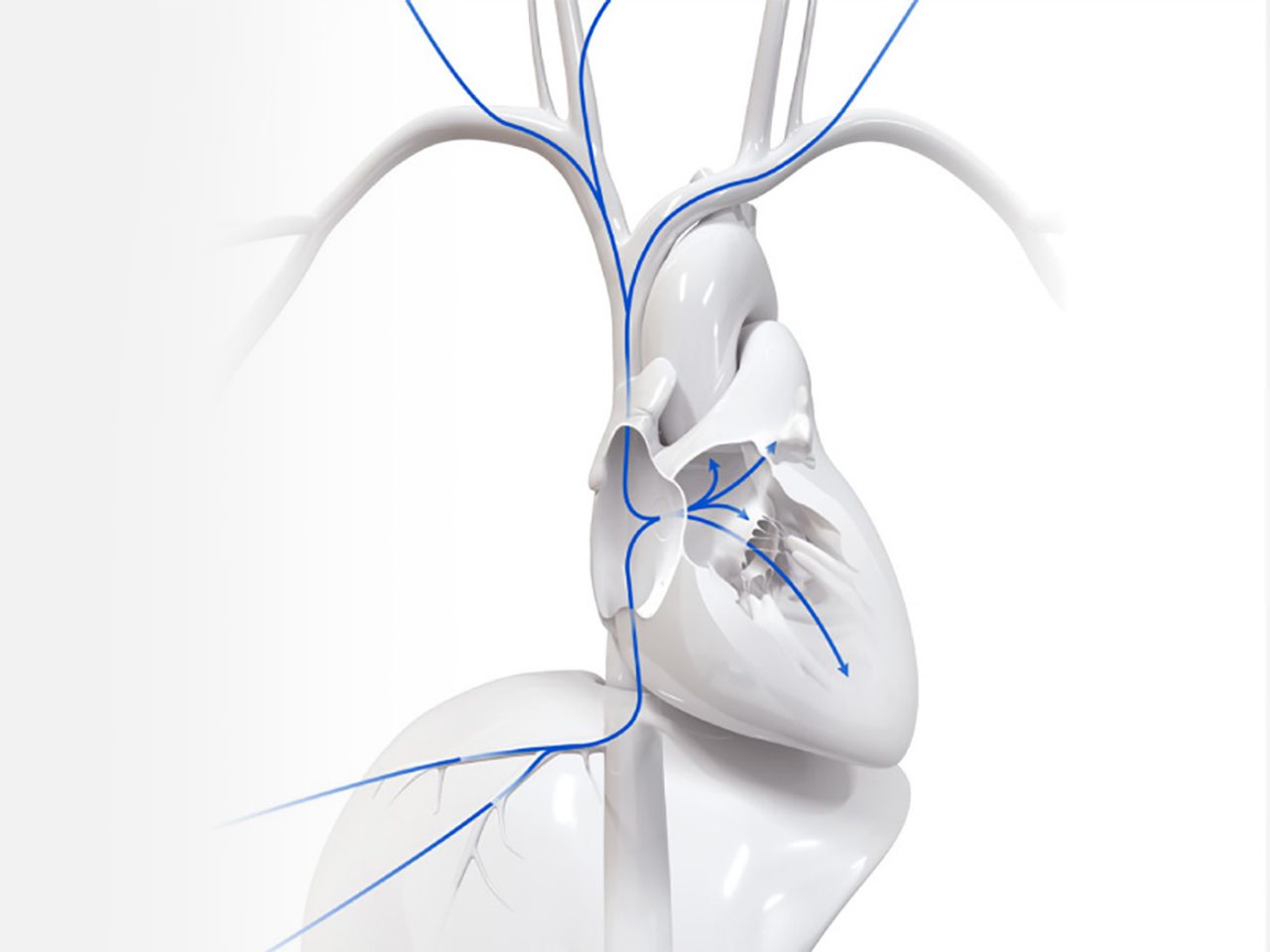
How it works
Animation of the SupraCross RF Transseptal Solution, a radiofrequency (RF) transseptal access device for alternate access into the LA
Why choose the SupraCross RF Solution
Achieve transseptal access using an alternate approach with the SupraCross Steerable Sheath and SupraCross RF Wire
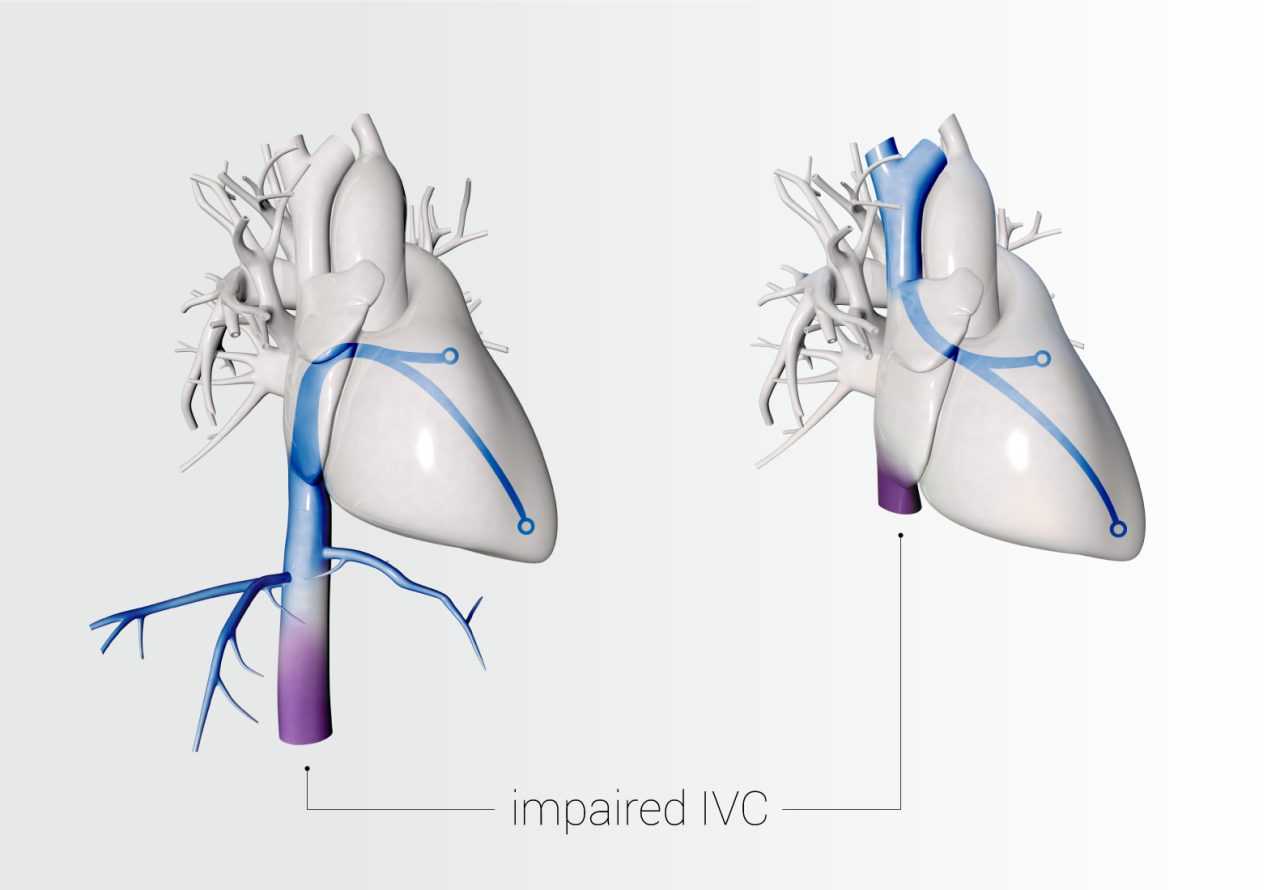
LA access from any approach
Optimized transseptal approach may be required for these procedures, which have been performed successfully via jugular venous and transhepatic approach in patients with impaired inferior vena cava:
- Mitral valve repair1
- Left ventricular tachycardia ablation2
- Pulmonary vein isolation3,4,5,6
- Left atrial appendage occlusion7
3-in-1 SupraCross RF Wire
High precision SupraCross Steerable Sheath
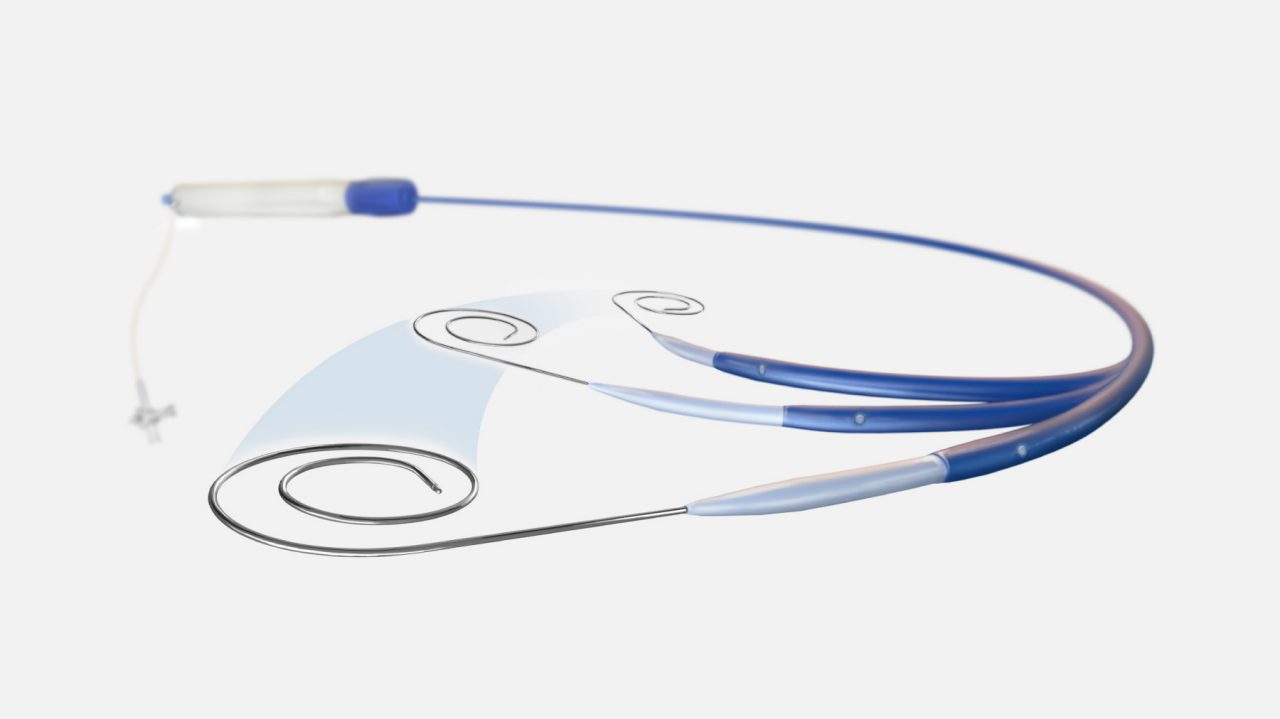
TruGlide™ handling
Responsive, smooth, high-precision steering to confidently position your curve
Flexible dilator
A fully steerable sheath with flexible dilator to facilitate the navigation of complex anatomy and precise positioning on the fossa4
What’s included
The SupraCross RF Transseptal Solution includes:
- SupraCross RF Wire
- SupraCross Steerable Sheath
- Single-use RFP-100A Connector Cable
- 0.035” mechanical guidewire
- Single-use connector cable, compatible with the RFP-100A RF Puncture Generator†
Required product
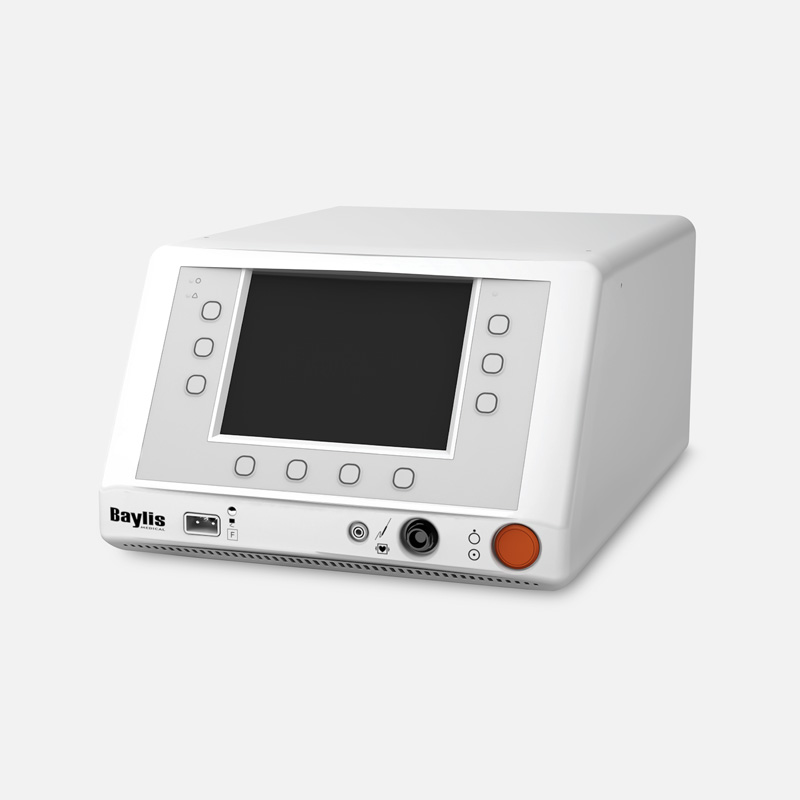

Designed for controlled tissue puncture using radiofrequency energy
Publication summaries
September 2020, Yap et al., published in Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions
This report described MitraClip™ device implantation via the transjugular approach in a patient with tortuous inferior vena cava and prior mitral valve annuloplasty.
April 2020, Hernandez-Ojeda et al., published in HeartRhythm Case Reports
This case report described successful pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) for persistent atrial fibrillation in a patient with interrupted inferior vena cava (IVC) and sinus node dysfunction associated with left atrial isomerism.
March 2020, Suryanarayana et al., published in HeartRhythm Case Reports
This case report described a novel technique for left atrial access and RF ablation using hepatic vein access in a patient with surgically ligated inferior vena cava.
January 2020, Liang et al., published in JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology
This study reported outcomes of transseptal puncture and atrial fibrillation ablation using dedicated RF tools via a superior approach in patients with interrupted or absent inferior vena cavas.
SupraCross RF Wire
| Feature | Specifications |
| Wire length | 180 cm |
| Outer diameter | 0.035” |
| Radiopaque marker | Platinum tungsten coil; 3 cm |
| Distal coil diameter | 2.4 cm |
Compatible with 0.035” dilators
SupraCross Steerable Sheath
| Feature | Specifications |
| French size | 8.5F |
| Sheath usable length | 45 cm |
| Sheath overall length | 65 cm |
| Dilator usable length | 67 cm |
| Compatible guidewire | 0.035” |
| Distal curve | Bidirectional (90° CCW, 180° CW) |
| Distal curve diameter | Small (17 mm), Medium (22 mm), Large (50 mm) |
Compatible with 12.5F introducers
Ordering information
| Product number | Steerable sheath | RF wire |
| SCAK0001 | SupraCross Sheath (Small) | SupraCross RF Wire |
| SCAK0002 | SupraCross Sheath (Medium) | SupraCross RF Wire |
| SCAK0003 | SupraCross Sheath (Large) | SupraCross RF Wire |
All SupraCross solutions also include:
- 0.035” mechanical guidewire
- Single-use connector cable, compatible with the RFP-100A RF Puncture Generator
Looking for more training? Contact our medical education team
In-person training
Explore in-person training opportunities for electrophysiologists and interventional cardiologists of all experience levels.
Online education
Online medical training and education courses
The EDUCARE online platform makes healthcare education and training more relevant, more comprehensive, more personal, and more accessible. Register to access a library of procedural videos, case studies, training resources, and events.
Brochure
All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
* Studies used NRG™ Transseptal Needle, which employs the same RF puncture technology as the SupraCross RF Wire.
† Baylis Medical Company Radiofrequency Puncture Generator RFP-100A
References:
1. Yap, J., et al. (2020). Transjugular mitral valve repair with the MitraClip: A step-by-step guide. Cath Cardiovasc Interv, 96(3), 699-705. doi: 10.1002/ccd.28902
2. Han, S., et al. (2013). Catheter ablation of left ventricular tachycardia through internal jugular vein: Refining the continuous line. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 24(5), 596-599. doi: 10.1111/jce.1204
3. Liang, J., et al. (2020). Radiofrequency-assisted transseptal access for atrial fibrillation ablation via a superior approach. JACC: Clin Electrophysiol, 6(3), 272-281. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2019.10.019
4. Santangeli, P., et al. (2020). How to perform left atrial transseptal access and catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation from a superior approach. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 31(1), 293-299. doi.org/10.1111/jce.14294
5. Baszko, A., et al. (2015). Transseptal puncture from the jugular vein and balloon cryoablation for atrial fibrillation in a patient with azygos continuation of an interrupted inferior vena cava. Europace, 17(7), 1153-1156. doi.org/10.1093/europace/euu413
6. Hernandez-Ojeda, J., et al. (2020). Transseptal access and pulmonary vein isolation via internal jugular veins for persistent atrial fibrillation treatment in a patient with left atrial isomerism, sinus node dysfunction, and interrupted inferior vena cava: The usefulness of robotic magnetic navigation. HeartRhythm Case Reports, 6(4), 210-214. doi: 10.1016/j.hrcr.2019.12.015
7. Aizer, A., et al. (2015). Three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography to facilitate transseptal puncture and left atrial appendage occlusion via upper extremity venous access. Circ Arrythm Electrophysiol, 8(4), 988-990. doi: 10.1161/ 0120CIRCEP.115.00278
8. Sharma, G., et al. (2016). Accuracy and procedural characteristics of standard needle compared with radiofrequency needle transseptal puncture for structural heart intervention. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. Epub doi: 10.1002/ccd.26608
9. Smelley, M.P., et al. (2010). Initial experience using a radiofrequency powered transseptal needle. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 21(4), 423-427.doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2009.01656