Boston Scientific accounts are for healthcare professionals only.

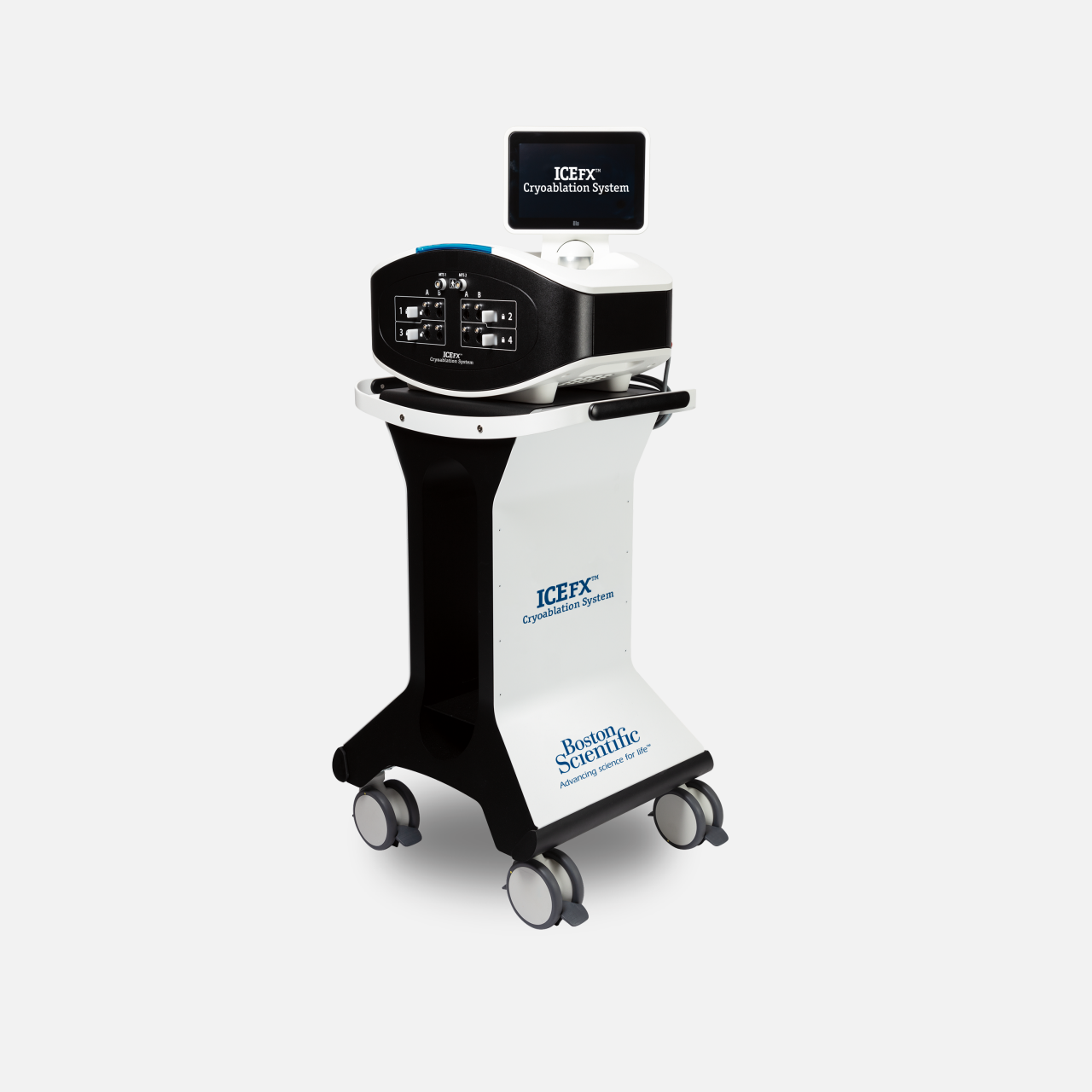
ICEfx™ Cryoablation System
Reimbursement
Configure or select a product to continue to order
- Overview
- Ordering information
- Training
- Resources
- Bone indication
- Kidney indication
- Lung indication
- Nerve indication
ICEfx™ Cryoablation System
The ICEfx Cryoablation System is the next generation of ablation systems with a compact design and interface that offers predictable and seamless therapy delivery.
How it works
Why use the ICEfx Cryoablation System and Needles
The ICEfx Cryoablation System is a next-generation system with an upgraded interface and argon-only gas.
Subscribe to receive product updates
Receive emails on the latest advances, clinical data and news.
Ordering information
ICEfx cryoablation system
| Catalog Number | ICEfx Cryoablation System and Accessories |
| FPRCH8000-02 | ICEfx System, Console only |
| FPRCH8010-02 | ICEfx Cart |
| FPRCH4000-02 | Dual Tank Cylinder Gas Adapter, 5M PSI |
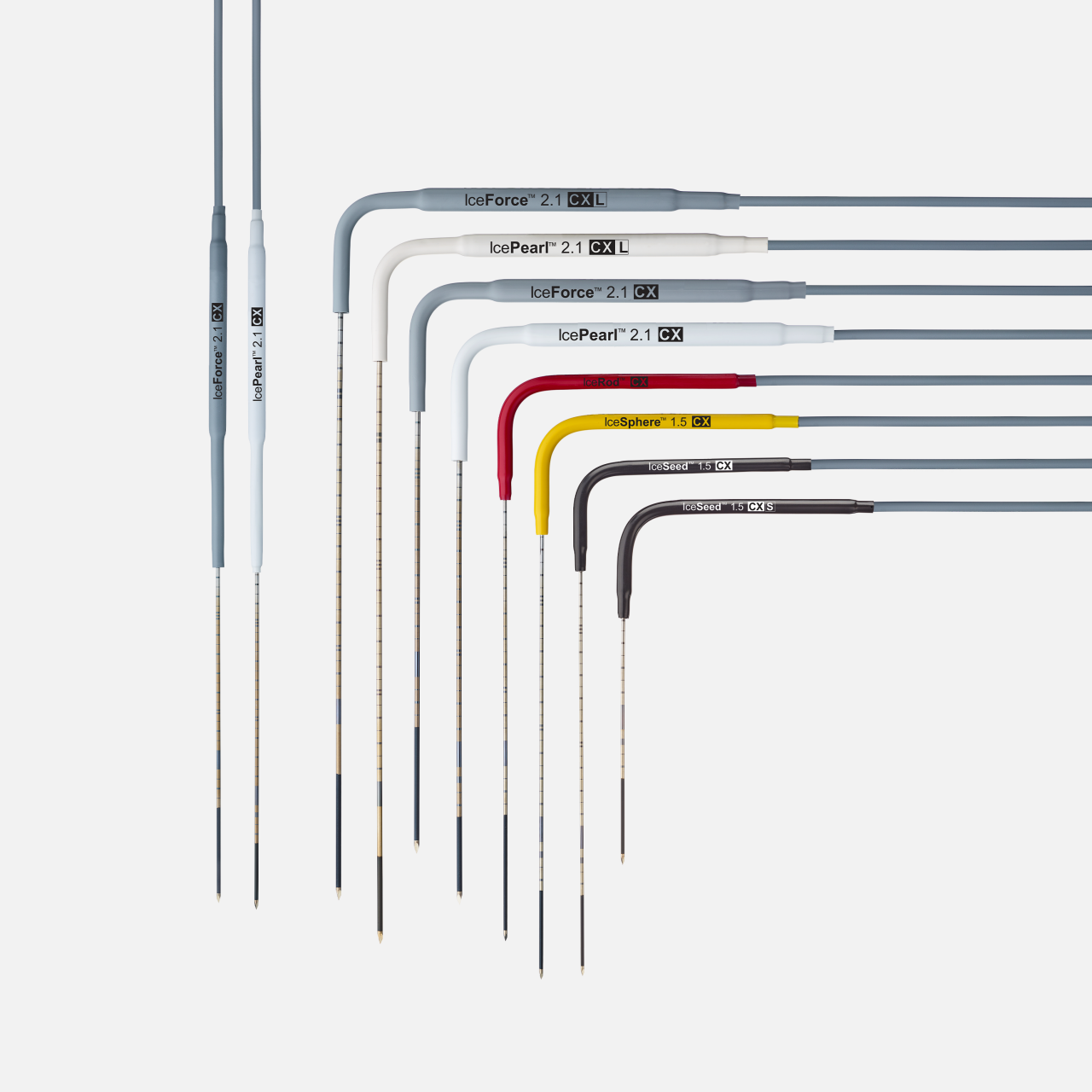
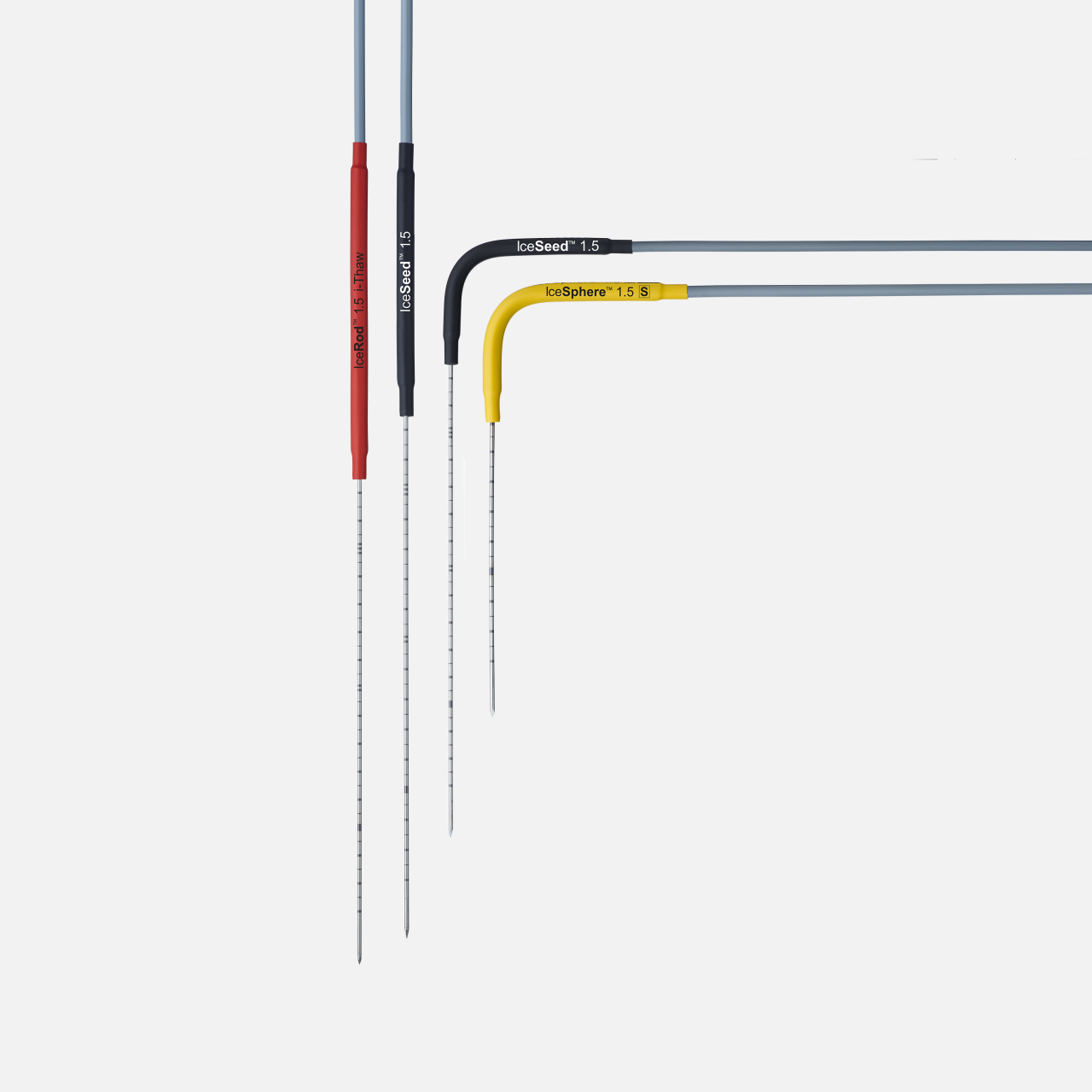
Classic cryoablation needles
| Cryoablation needles | Part number | Configuration | Shaft diameter (mm / gauge) | Shaft Length (cm) | Handle Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IceSeed™ 1.5 | FPRPR3202 | Angled 90º | 1.5 mm / 17 G | 17.5 cm | Black |
| IceSeed™ 1.5 | FPRPR3201 | Straight | 1.5 mm / 17 G | 17.5 cm | Black |
| IceSphere™ 1.5 S | FPRPR3561 | Angled 90º | 1.5 mm / 17 G | 17.5 cm | Yellow |
| IceRod™ 1.5 I-Thaw | FPRPR4009 | Straight | 1.5 mm / 17 G | 17.5 cm | Red |
CX cryoablation needles
| Cryoablation needles | Part number | Configuration | Shaft diameter (mm / gauge) | Shaft Length (cm) | Handle color | Track ablation radial width / length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IcePearl™ 2.1 CX | FPRPR3603 | Straight | 2.1 mm / 14 G | 17.5 cm | White | 2.1 / 13 mm |
| IcePearl™ 2.1 CX | FPRPR3601 | Angled 90º | 2.1 mm / 14 G | 17.5 cm | White | 2.1 / 13 mm |
| IcePearl™ 2.1 CX L | FPRPR3617 | Angled 90º | 2.1 mm / 14 G | 23 cm | White | 2.1 / 13 mm |
| IceForce™ 2.1 CX | FPRPR3604 | Straight | 2.1 mm / 14 G | 17.5 cm | Gray | 2.5 / 29 mm |
| IceForce™ 2.1 CX | FPRPR3602 | Angled 90º | 2.1 mm / 14 G | 17.5 cm | Gray | 2.5 / 29 mm |
| IceForce™ 2.1 CX L | FPRPR3618 | Angled 90º | 2.1 mm / 14 G | 23 cm | Gray | 2.5 / 29 mm |
| IceRod™ 1.5 CX | H7493968535330 | Straight | 1.5 mm / 17 G | 17.5 cm | Red | 1.7 / 14 mm |
| IceRod™ 1.5 CX | FPRPR3533 | Angled 90º | 1.5 mm / 17 G | 17.5 cm | Red | 2.3 / 30 mm |
| IceSphere™ 1.5 CX | H7493968435730 | Straight | 1.5 mm / 17 G | 17.5 cm | Yellow | 1.6 / 14 mm |
| IceSphere™ 1.5 CX | FPRPR3573 | Angled 90º | 1.5 mm / 17 G | 17.5 cm | Yellow | 1.7 / 14 mm |
| IceSeed™ 1.5 CX | H7493968333170 | Straight | 1.5 mm / 17 G | 17.5 cm | Black | 1.6 / 14 mm |
| IceSeed™ 1.5 CX | H7493967433170 | Angled 90º | 1.5 mm / 17 G | 17.5 cm | Black | 1.6 / 14 mm |
| IceSeed™ 1.5 CX S | H7493967233100 | Angled 90º | 1.5 mm / 17 G | 10 cm | Black | 1.6 / 14 mm |
Training resources
Sign up to learn about Boston Scientific events and cryoablation education opportunities for bone, kidney, lung and nerve indications.
Online medical training and education courses
The EDUCARE online platform makes healthcare education and training more relevant, more comprehensive, more personal, and more accessible. Register to access a library of procedural videos, case studies, training resources, and events.
ICEfx Brochure
Learn about the ICEfx Cryoablation System offering reliable performance and ease of operation, featuring customizable cycle programming, adjustable freeze cycles, and a user-friendly interface for precise iceball control.
Needles Brochures
Learn about the IceSeed CX Needles, which can treat various tumors and lesions with a shorter shaft for sculptable iceball size.
Learn about the proprietary design of CX Needles, offering precise placement and helium-free thaw, which reduce setup time and costs.
CX Needles Isotherm Guide
Use the isotherm guide to aid in treatment planning. View isotherm sizes for CX Needles, ranging from 1 to 4 needles used.
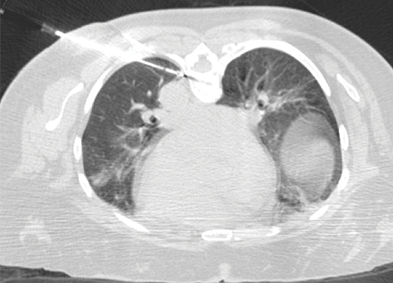
Bone cryoablation
Treating Painful Bone Metastases with Cryoablation: Esther’s Story
Bone is the most common site of metastatic cancer. Bone metastasis are associated with bone pain resulting in significant decreased physical function and quality of life (QOL). External beam radiation therapy is the standard for treatment of patients with painful bone metastases, along with opioids and non-opioid analgesics. Unfortunately, the time to pain relief for radiation therapy is 1-2 months and for many patients the pain can persist after radiation therapy. Cryoablation for painful bone metastases allows for rapid and durable pain palliation.
The MOTION study
Cryoablation for Palliation of Painful Bone Metastases: The MOTION Multicenter Study
This multicenter, prospective, single arm, phase II study examined the impact of the treatment of a painful bone metastatic lesion in each patient.
Study objective
- The primary objective was to evaluate the efficacy of cryoablation for pain palliation of bone metastases from baseline to 8 weeks after cryoablation in worst pain in the last 24 hours.
- Separate evaluations of ancillary efficacy endpoints were also made through 24 weeks.
Key results
Figure 1
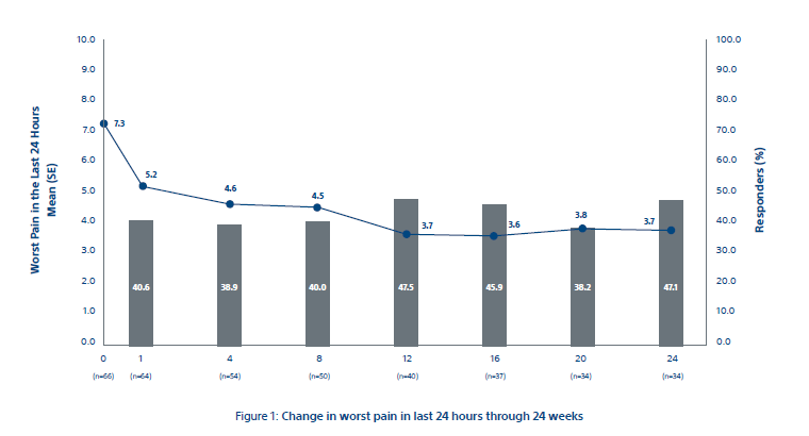
The primary efficacy endpoint of mean change in worst pain in last 24 hours from baseline to week 8 was 2.61 ± 0.43 points (95% CI: -3.45, -1.78) as shown in Figure 1. Clinically meaningful changes from baseline were observed at all time points after week 8. In the completed case analysis (n = 64), mean pain scores improved by 2 points as early as week 1 and continued through week 24 and the 92% of participants achieved palliation (59/64), with median time to maximal pain relief of 39.0 days (95% CI: 43.7, 72.4 days; n = 59). Most participants achieved their maximum palliation by week 1 (33.9%; 20 of 59), week 4 (25.4%; 15 of 59), or week 12 (15.3%; nine of 59).
Figure 2
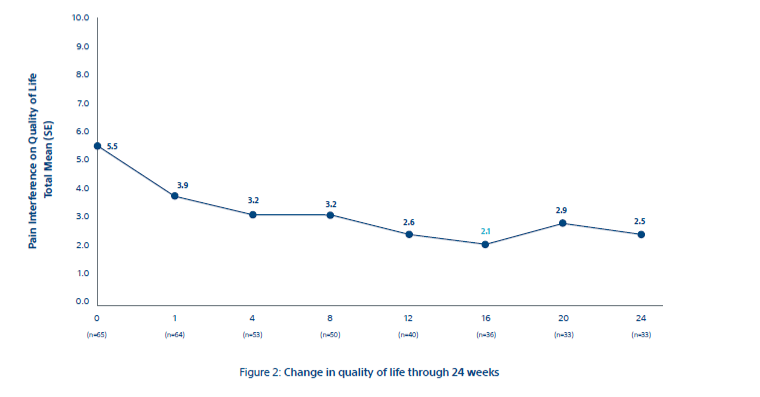
Quality of life consistently improved over 6 months (Fig 2). The overall treatment effect was rated “better than at the last visit” by 60.9% (39 of 64) and 30% (11 of 37) of participants at weeks 1 and 24, respectively; treatment effect was rated “worse than at the last visit” by 13% (eight of 64) and 11% (four of 37) participants at weeks 1 and 24, respectively.
Conclusion
Overall, the data shows a rapid and durable pain relief along with a decrease in MEDD and a corresponding increase in the quality of life for patients.
Bone resources
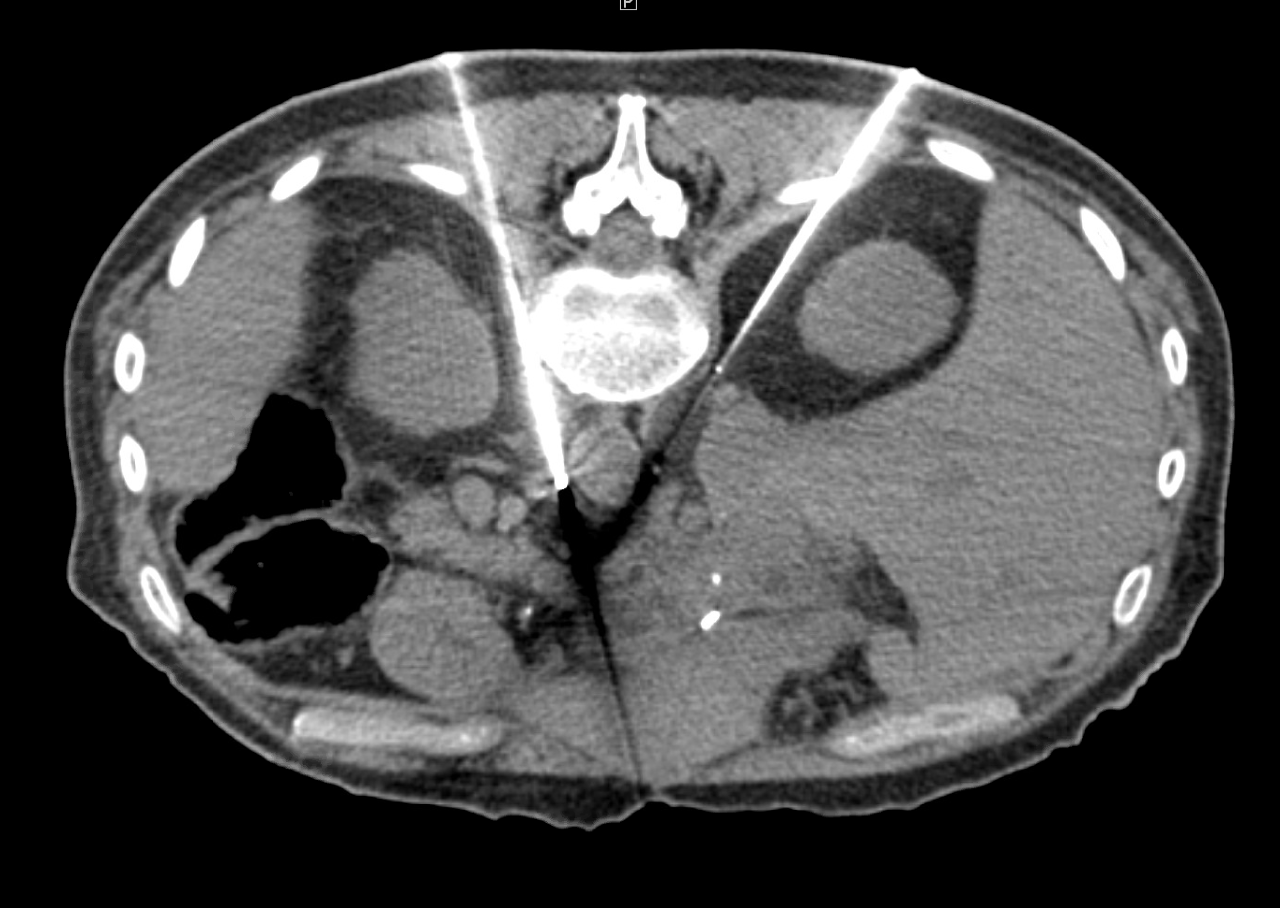
Kidney cryoablation
Percutaneous cryoablation (PCA) for renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has grown rapidly over the last decade. This is due in large part to a growing body of evidence demonstrating comparable outcomes with partial nephrectomy, but with decreased complications and greater preservation of renal function. Similarly, cryoablation has an advantage over heat-based ablation modalities, allowing for visualization of the ablation zone and preservation of critical structures, even in central lesions.
EuRECA study overview
The largest, prospective, real-world, multicenter, multidisciplinary study on the use of cryoablation for treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in 1700 patients.
Urology Initiated
A joint mission between urologists and interventional radiologists and administered through the Bristol Urological Institute
Over 1400 biopsy-proven RCC patients
Data from over 900 treatments with biopsy-proven RCC with an almost 5-year follow-up
15 centers across 5 European countries
This Boston Scientific sponsored study began in 2014 and ended in 2020.
Outcomes comparison
How do cryoablation and ablation compare to partial nephrectomy across key outcomes?
| Metric | How does cryo/ablation compare to partial nephrectomy (PN) | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Local recurrence free survival* | Level 1 data needed | Older data, meta-analyses include RF |
| Metastatic-free survival* | Ablation = PN | |
| Cancer-specific survival* | Ablation = PN | |
| Overall survival* | Level 1 data needed | Selection bias - ablation patients tend to be older with more comorbidities |
| Renal Function | Cryo/ablation > PN | |
| Safety | Cryo/ablation > PN | |
| Cost | Cryo/ablation > PN | |
| Quality of life | Cryo/ablation > PN |
*Oncological outcomes: Similar = | Better >
Case studies
Kidney resources
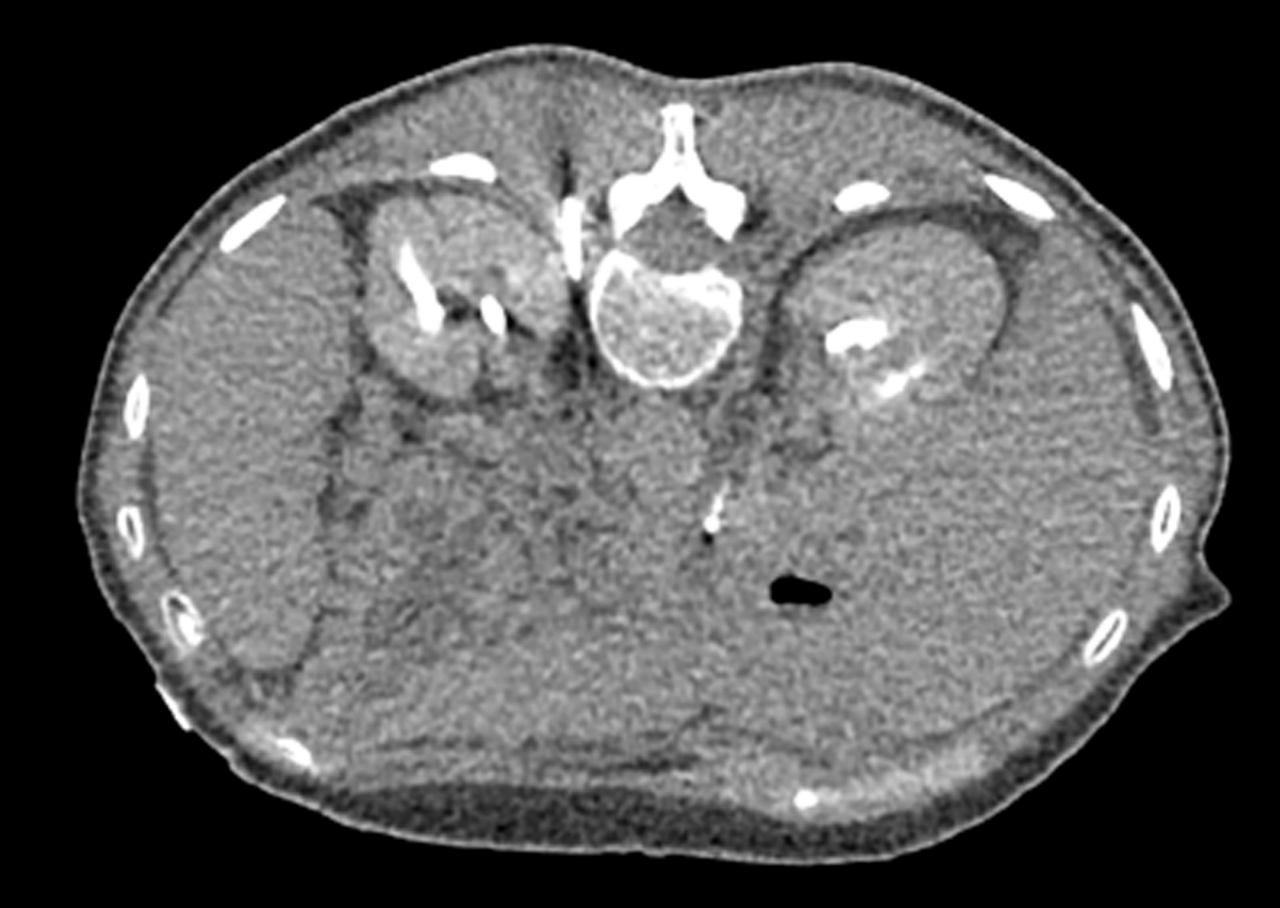
Lung cryoablation
Percutaneous cryoablation (PCA) is a tool for treating primary and metastatic lung tumors. Typically, patients are non-surgical candidates with primary non-small cell or oligometastatic lung cancer. Lung cryoablation preserves pulmonary function, offers repeatability for future metastases, and can treat multiple lung tumors during a single treatment. Unlike other ablative treatments, cryoablation provides excellent local tumor control. Patients typically have a short hospital stay and report low incidence of pre-procedural and post-procedural pain.
The ECLIPSE study
Efficacy of Cryoablation on Metastatic Lung Tumors with a 5-Year Follow-up
Study objective
- Primary objective was to assess 5-year local control of CA in lung tumors of 3.5 cm or less in patients with pulmonary metastatic disease
- Secondary objectives to evaluate cancer-specific and overall survival, as well as evaluate changes in quality of life (QoL) over a five-year period
Key results
Local Tumor Control Rates
94.2%
1 year
87.9%
3 years
79.2%
5 years
Freedom from local progression
Patients free from local progression without additional locoregional treatment at the index lesion.
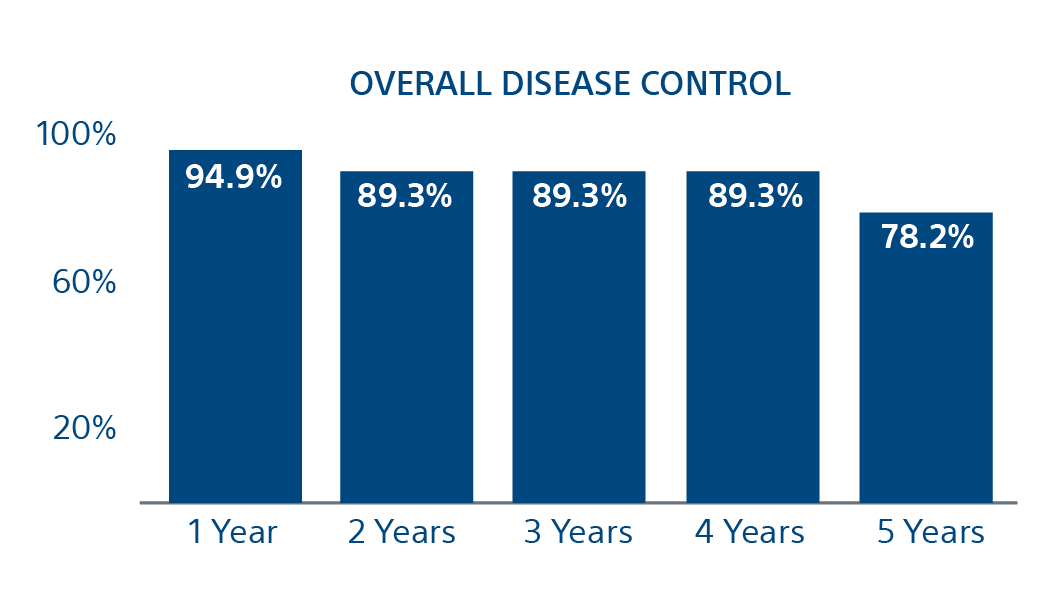
78.2%
Freedom of Local Progression at 5 years
(95% CI = 91.4, 98.4; number at risk [N} = 37)
(95% CI = 84.3, 94.4; N = 30)
(95% CI = 84.3, 94.4; N = 23)
(95% CI = 84.3, 94.4; N = 21)
(95% CI = 66.8, 89.5; N = 7)
Conclusion
Cryoablation is an effective means of local tumor control in patients with metastatic lung disease, with the majority of surviving patients maintaining local tumor control at the index tumor site over 5 years. Furthermore, cancer-specific survival and overall survival were greater after 5 years than for many other local treatment modalities, including surgical resection.
Case study
Lung resources
Nerve cryoablation
Due to the opioid crisis, there is a growing need for alternate pain palliation methods for hard-to-treat neuropathies. Because of this, Interventional Radiologists (IRs) are playing an increasing role in the pain management space. The IR’s ability to percutaneously access otherwise unreachable nervous system structures, visualize and monitor ablation zones, and induce predictable neuroregeneration in clinical settings has unlocked a multitude of opportunities.
Cryoneurolysis nerve targets
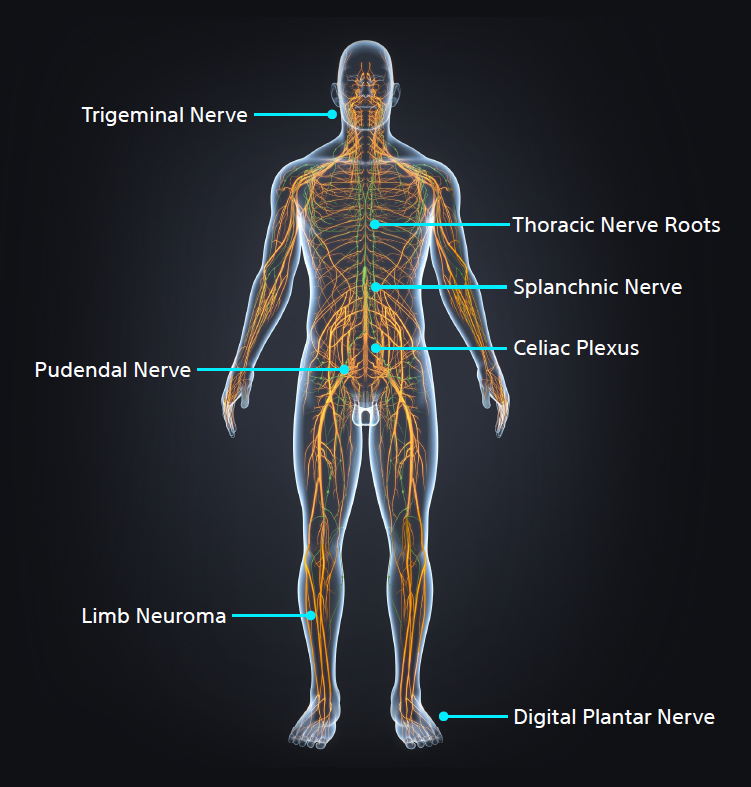
Interventional Radiologists must be aware of key nerve targets, have an in-depth understanding of which patients are candidates for image-guided percutaneous cryoneurolysis (PCA), and the differentiators between cryoablation and heat or alcohol-based neurolysis.
- Pudendal Nerve
- Morton's Neuroma
- Dorsal Neuropathies
- Limb Neuroma
- Celiac Plexus
- Trigeminal Nerve
- Spanchnic Nerve