Boston Scientific accounts are for healthcare professionals only.

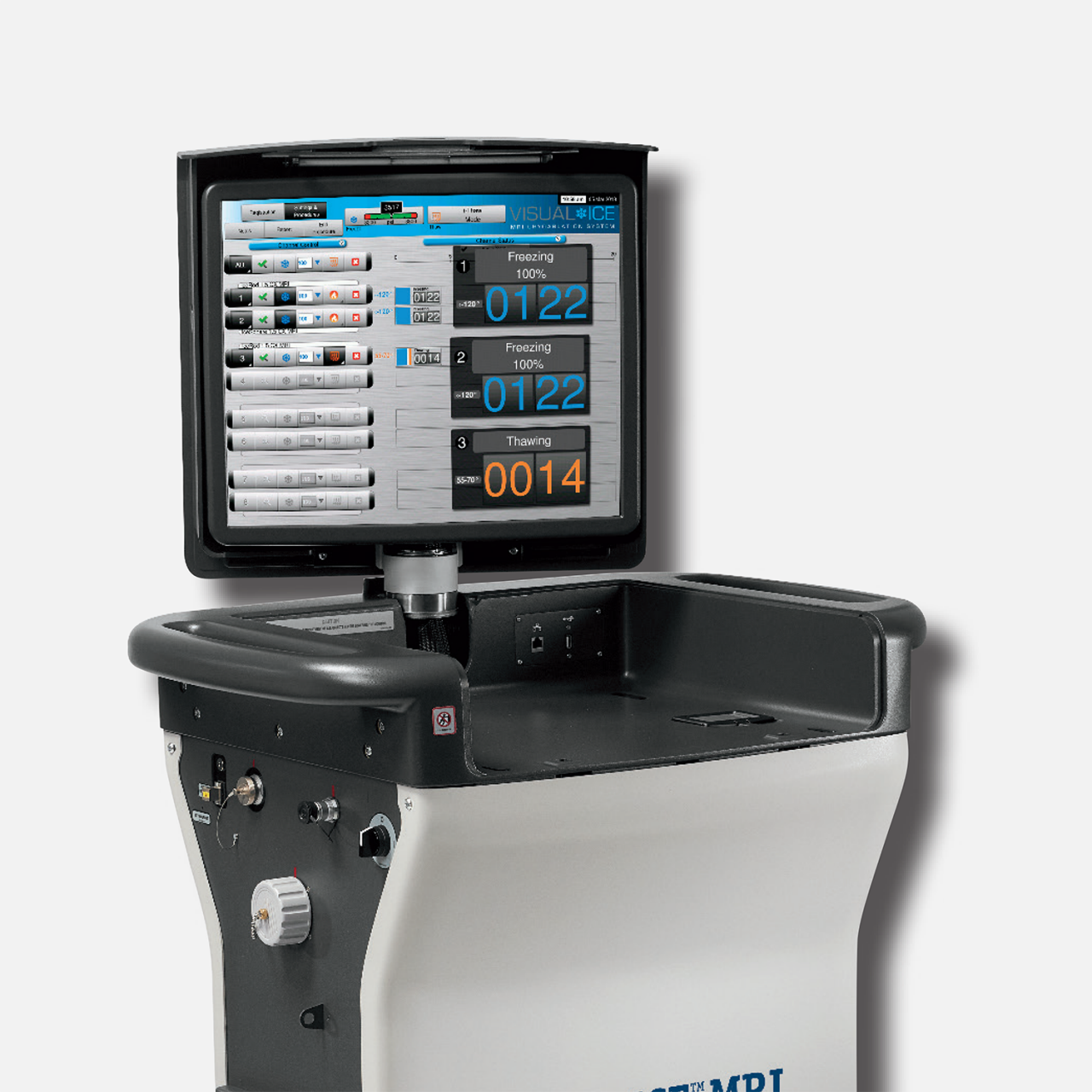
VISUAL ICE™ MRI Cryoablation System
Reimbursement
Configure or select a product to continue to order
- Overview
- Ordering information
- Training
- Resources
- Kidney indication
- Lung indication
- Nerve indication
The Visual ICE™ MRI Cryoablation System
Specialized for the magnet room, the Visual ICE MRI Cryoablation System is the only ablation system that leverages the unique advantages of cryoablation zone visibility with the exquisite image resolution of MR.
How it works
Learn about the cryoablation mechanism of action and how it's used to target tumors.
Why use the Visual ICE MRI Cryoablation System and Needles
Subscribe to receive product updates
Receive emails on the latest advances, clinical data and news.
References
- van Oostenbrugge TJ, Langenhuijsen JF, Overduin CT, et al. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2017; 28(8): 1098-1107
- Overduin CG, Jenniskens SFM, Sedelaar JPM, et al. Eur Radiol 2017; 27(11): 4828-483
- Sewell PE, Howard JC, Shingleton WB, Harrison RB. South Med J 2003; 96(7): 708-710
- Tatli S, Acar M, Tuncali K, et al. Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16(1): 90-95
- Gangi A, Tsoumakidou G, Abdelli O, et al. Eur Radiol 2012; 22(8): 1829-1835
- Aghayev A, Tatli S. Expert Rev Med Devices 2014; 11(1): 41-52
- Glazer DI, Tatli S, Shyn PB, et al. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2017; 209(6): 1381-1389
- Kinsman KA, White ML, Mynderse LA. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2017; doi: 10.1007/s00270-017-1799-6
- Woodrum DA, Kawashima A, Gorny KR, Mynderse LA. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 2015; 23(4): 607-619
- Woodrum DA, Kawashima A, Karnes RJ. Urology 2013; 82(4): 870-875
Ordering information
Visual ICE MRI cryoablation system
| Catalog Number | Visual ICE™ MRI System and Accessories | Description |
|---|---|---|
| H7493961070000 | Visual ICE™ MRI Cryoablation System | A cryoablation system with built-in gas pressure regulators; two flexible gas supply lines (one argon, one helium) with pressure gauges; a system cover |
| H7493970071000 | Visual ICE™ MRI Mobile Connection Panel | A Visual ICE™ MRI remote Mobile Connection Panel to support MRI needle connections in magnet room; a Mobile Connection Panel cover |
| H7493969970500 | Visual ICE™ MRI Junction Box Assembly | Two Visual ICE™ MRI Junction Box Assemblies containing gas, electrical and fiber optic connectors; One Penetration Panel |
| ASM7005 | Visual ICE™ MRI Junction Box Harness (5 m) | One Visual ICE™ MRI Junction Box Harness (5 m) containing gas, electrical and fiber optic lines and connectors, packed in a protective case |
| ASM7010 | Visual ICE™ MRI Junction Box Harness (10 m) | One Visual ICE™ MRI Junction Box Harness (10 m) containing gas, electrical and fiber optic lines and connectors, packed in a protective case |
| ASM7015 | Visual ICE™ MRI Junction Box Harness (15 m) | One Visual ICE™ MRI Junction Box Harness (15 m) containing gas, electrical and fiber optic lines and connectors, packed in a protective case |
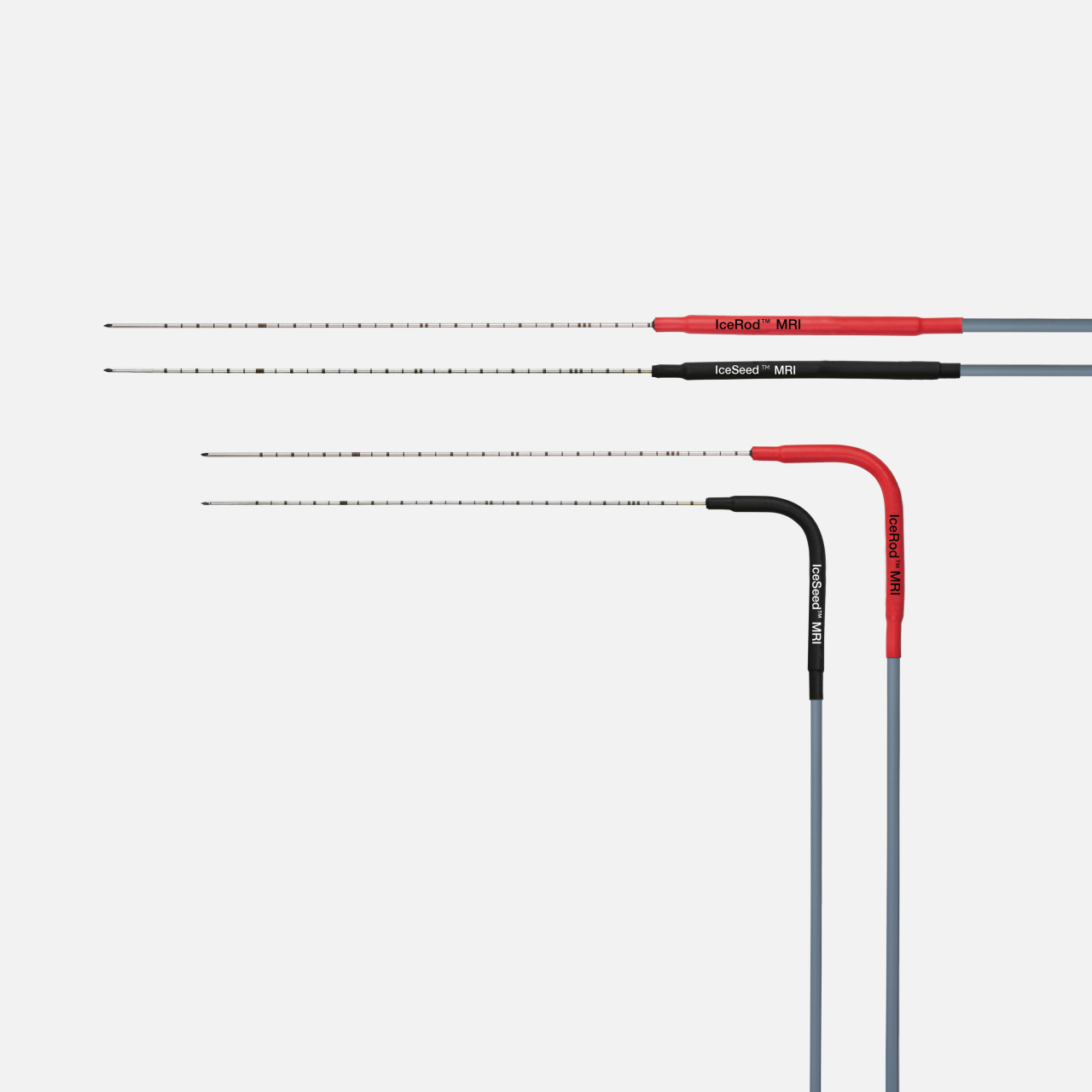
Classic MRI cryoablation needle details
| Classic MRI Needle Details | Catalog Number | Shaft Length (cm) / Gauge (G) | Active Thaw |
|---|---|---|---|
| IceSeed™ 1.5 MRI Cryoablation Needle | FPRPR3192 | 17.5 / 17 | Helium |
| IceSeed™ 1.5 MRI 90° Cryoablation Needle | FPRPR3194 | 17.5 / 17 | Helium |
| IceRod™ 1.5 MRI Cryoablation Needle | FPRPR3193 | 17.5 / 17 | Helium |
| IceRod™ 1.5 MRI 90° Cryoablation Needle | FPRPR3195 | 17.5 / 17 | Helium |
Training resources
Sign up to learn about Boston Scientific events and cryoablation education opportunities for bone, kidney, lung and nerve indications.
Online medical training and education courses
The EDUCARE online platform makes healthcare education and training more relevant, more comprehensive, more personal, and more accessible. Register to access a library of procedural videos, case studies, training resources, and events.
Visual ICE MRI Brochure
Learn about the Visual ICE MRI Cryoablation System offering a unique integration of cryoablation zone visibility with MR image resolution for precise and effective treatments.
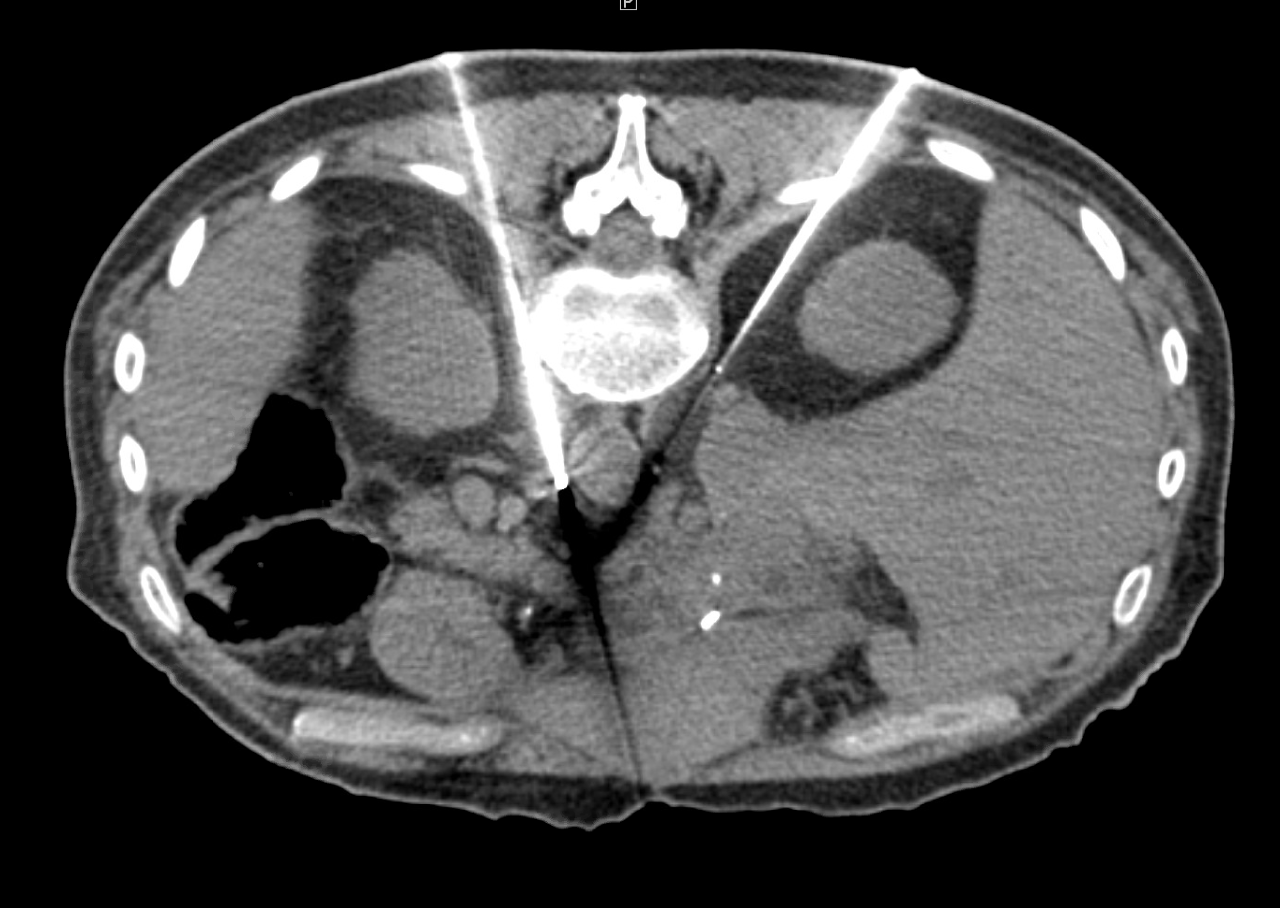
Kidney cryoablation
Percutaneous cryoablation (PCA) for renal cell carcinoma (RCC) has grown rapidly over the last decade. This is due in large part to a growing body of evidence demonstrating comparable outcomes with partial nephrectomy, but with decreased complications and greater preservation of renal function. Similarly, cryoablation has an advantage over heat-based ablation modalities, allowing for visualization of the ablation zone and preservation of critical structures, even in central lesions.
EuRECA study overview
The largest, prospective, real-world, multicenter, multidisciplinary study on the use of cryoablation for treatment of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in 1700 patients.
Urology Initiated
A joint mission between urologists and interventional radiologists and administered through the Bristol Urological Institute
Over 1400 biopsy-proven RCC patients
Data from over 900 treatments with biopsy-proven RCC with an almost 5-year follow-up
15 centers across 5 European countries
This Boston Scientific sponsored study began in 2014 and ended in 2020.
Outcomes comparison
How do cryoablation and ablation compare to partial nephrectomy across key outcomes?
| Metric | How does cryo/ablation compare to partial nephrectomy (PN) | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Local recurrence free survival* | Level 1 data needed | Older data, meta-analyses include RF |
| Metastatic-free survival* | Ablation = PN | |
| Cancer-specific survival* | Ablation = PN | |
| Overall survival* | Level 1 data needed | Selection bias - ablation patients tend to be older with more comorbidities |
| Renal Function | Cryo/ablation > PN | |
| Safety | Cryo/ablation > PN | |
| Cost | Cryo/ablation > PN | |
| Quality of life | Cryo/ablation > PN |
*Oncological outcomes: Similar = | Better >
Case studies
Kidney resources
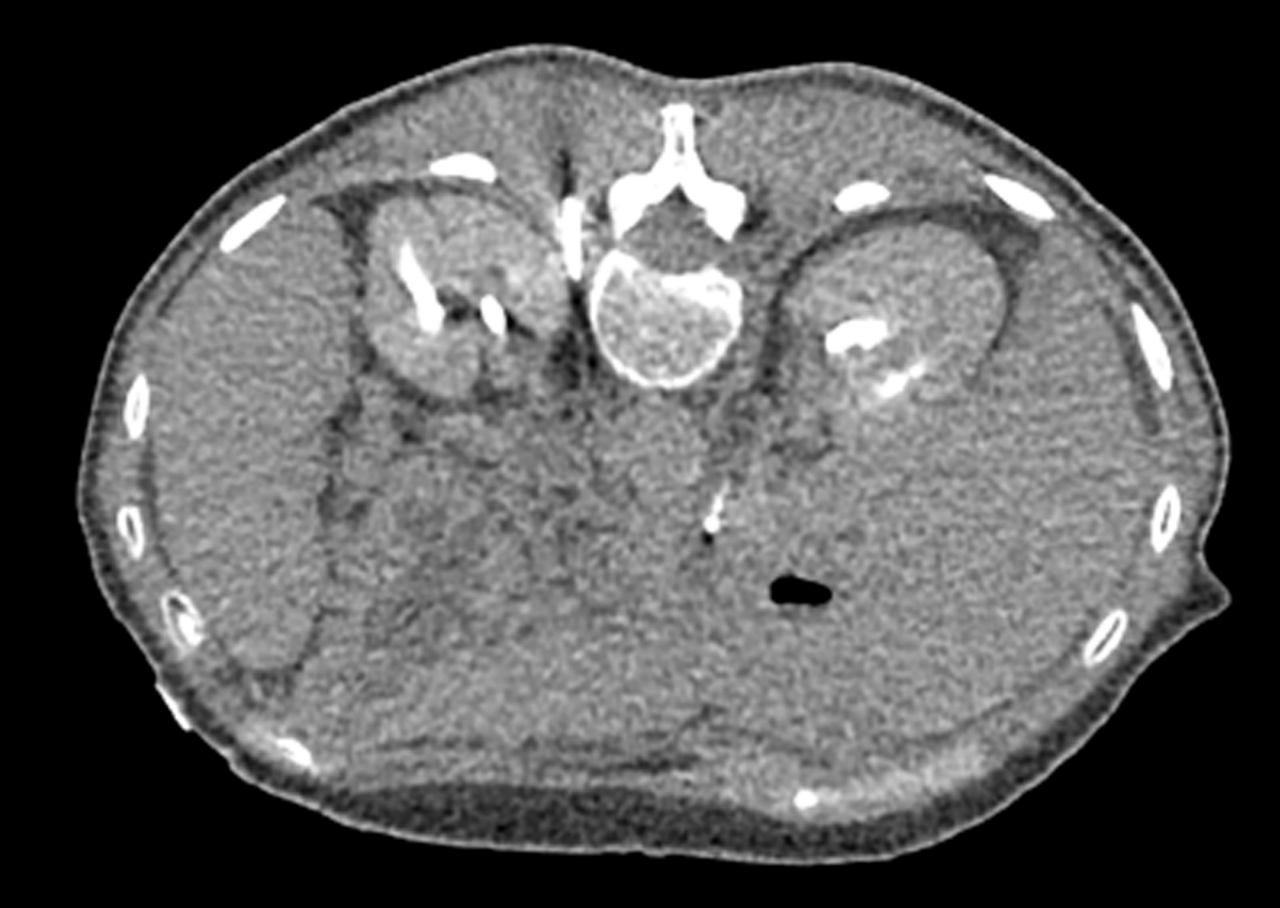
Lung cryoablation
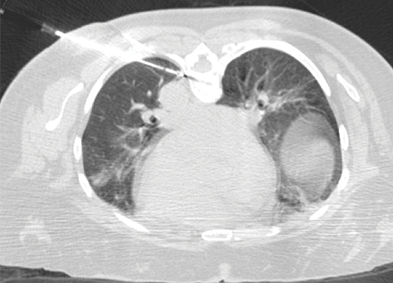
Percutaneous cryoablation (PCA) is a tool for treating primary and metastatic lung tumors. Typically, patients are non-surgical candidates with primary non-small cell or oligometastatic lung cancer. Lung cryoablation preserves pulmonary function, offers repeatability for future metastases, and can treat multiple lung tumors during a single treatment. Unlike other ablative treatments, cryoablation provides excellent local tumor control. Patients typically have a short hospital stay and report low incidence of pre-procedural and post-procedural pain.
The ECLIPSE study
Efficacy of Cryoablation on Metastatic Lung Tumors with a 5-Year Follow-up
Study objective
- Primary objective was to assess 5-year local control of CA in lung tumors of 3.5 cm or less in patients with pulmonary metastatic disease
- Secondary objectives to evaluate cancer-specific and overall survival, as well as evaluate changes in quality of life (QoL) over a five-year period
Key results
Local Tumor Control Rates
94.2%
1 year
87.9%
3 years
79.2%
5 years
Freedom from local progression
Patients free from local progression without additional locoregional treatment at the index lesion.
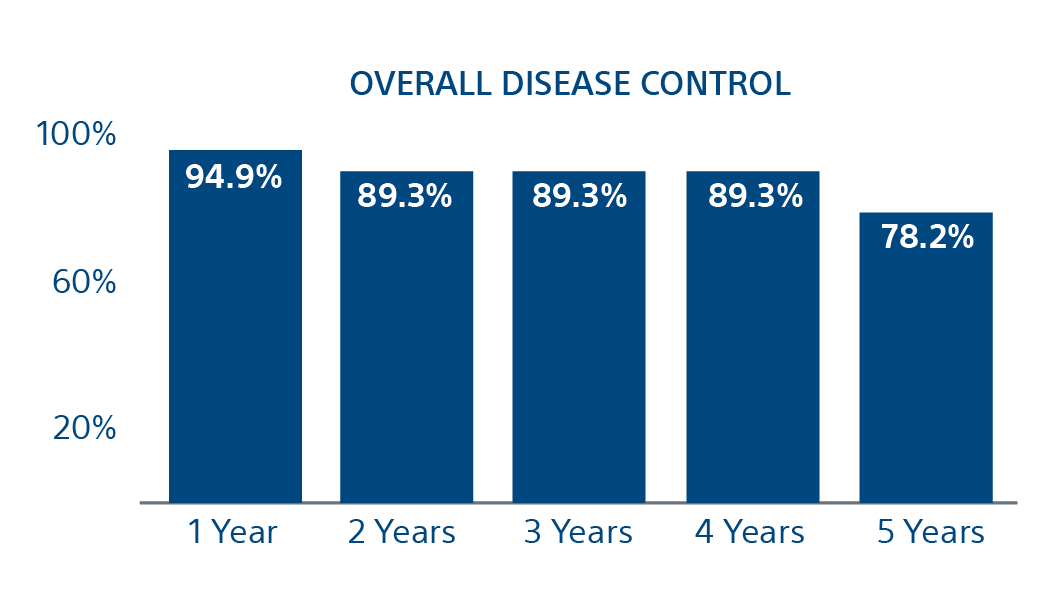
78.2%
Freedom of Local Progression at 5 years
(95% CI = 91.4, 98.4; number at risk [N} = 37)
(95% CI = 84.3, 94.4; N = 30)
(95% CI = 84.3, 94.4; N = 23)
(95% CI = 84.3, 94.4; N = 21)
(95% CI = 66.8, 89.5; N = 7)
Conclusion
Cryoablation is an effective means of local tumor control in patients with metastatic lung disease, with the majority of surviving patients maintaining local tumor control at the index tumor site over 5 years. Furthermore, cancer-specific survival and overall survival were greater after 5 years than for many other local treatment modalities, including surgical resection.
Case study
Lung resources
Nerve cryoablation
Due to the opioid crisis, there is a growing need for alternate pain palliation methods for hard-to-treat neuropathies. Because of this, Interventional Radiologists (IRs) are playing an increasing role in the pain management space. The IR’s ability to percutaneously access otherwise unreachable nervous system structures, visualize and monitor ablation zones, and induce predictable neuroregeneration in clinical settings has unlocked a multitude of opportunities.
Cryoneurolysis nerve targets
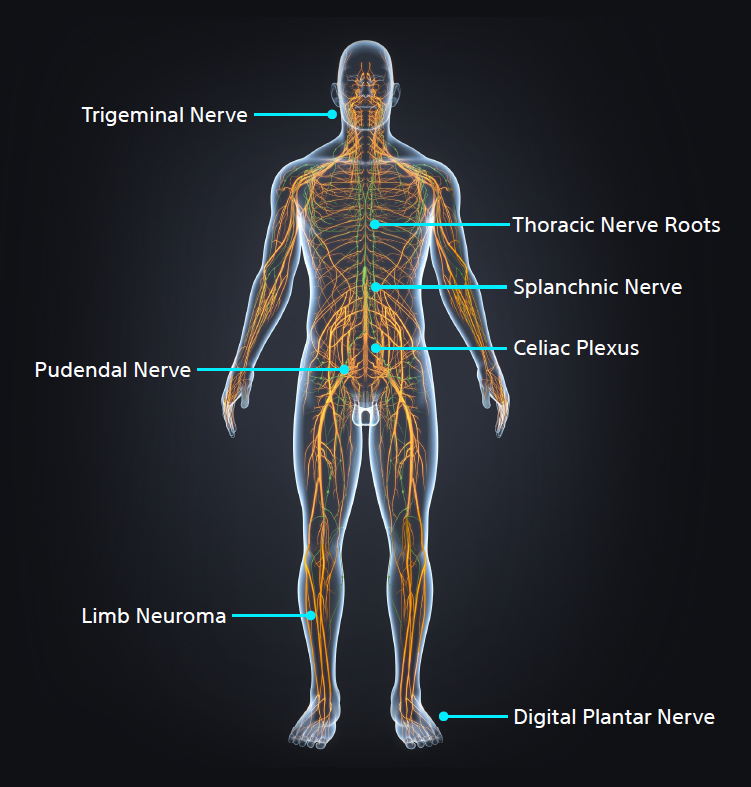
Interventional Radiologists must be aware of key nerve targets, have an in-depth understanding of which patients are candidates for image-guided percutaneous cryoneurolysis (PCA), and the differentiators between cryoablation and heat or alcohol-based neurolysis.
- Pudendal Nerve
- Morton's Neuroma
- Dorsal Neuropathies
- Limb Neuroma
- Celiac Plexus
- Trigeminal Nerve
- Spanchnic Nerve