Boston Scientific accounts are for healthcare professionals only.
No two lesions are the same
More patients are presenting with advanced disease and comorbidities.1 Common challenges include bifurcation, severe calcium, and in-stent restenosis (ISR). Effective lesion preparation is crucial for optimal outcomes.

Chart: A 12-year study analyzing PCI procedures (N = 20,301) reveals a significant rise in complex PCI procedures (5,647, 27.8% of total cases), primarily driven by interventions for bifurcations and left main arteries (P < 0.01).
Optimal treatment for calcified lesions is necessary
Over 30% of patients treated for PCI in the United States have some degree of calcium, a 31% increase over the last two decades.2 Calcium can make it difficult to dilate the artery, leading to complications such as dissection, inadequate stent expansion, and stent malapposition. Patients with moderate to severe calcium have a significantly higher risk of complications, including:
PRE-PCI
PERI-PCI
POST-PCI
A simplified calcium solution
The Calcium Lesion Modification Strategy (CLMS)7 is a simplified and highly effective approach to modifying calcific lesions. Based on proven research and clinical evidence, and vetted by expert interventional cardiologists, the CLMS is built on three key components shared by successful calcium algorithms:
A step-by-step guide

If the device does not pass, treat with rotational atherectomy. If the device passes or the vessel is undilatable (1:1 size), begin to IVUS.

Measure: lesion location (ostial; establish lesion length and define landing zones), plaque morphology (arc: <270° vs. >270°; extent of disease: focal vs. diffuse), and vessel size MLD (<2mm vs. > 2mm).

If larger MLD device delivers eccentric arc <180°: modify calcium with a Cutting Balloon, if a smaller MLD ostial/diffuse preferred concentric arc >270°: modify calcium with Rotational Atherectomy; if a larger MLD ostial/focal preferred concentric arc >270°: modify calcium with Intravascular Lithotripsy.
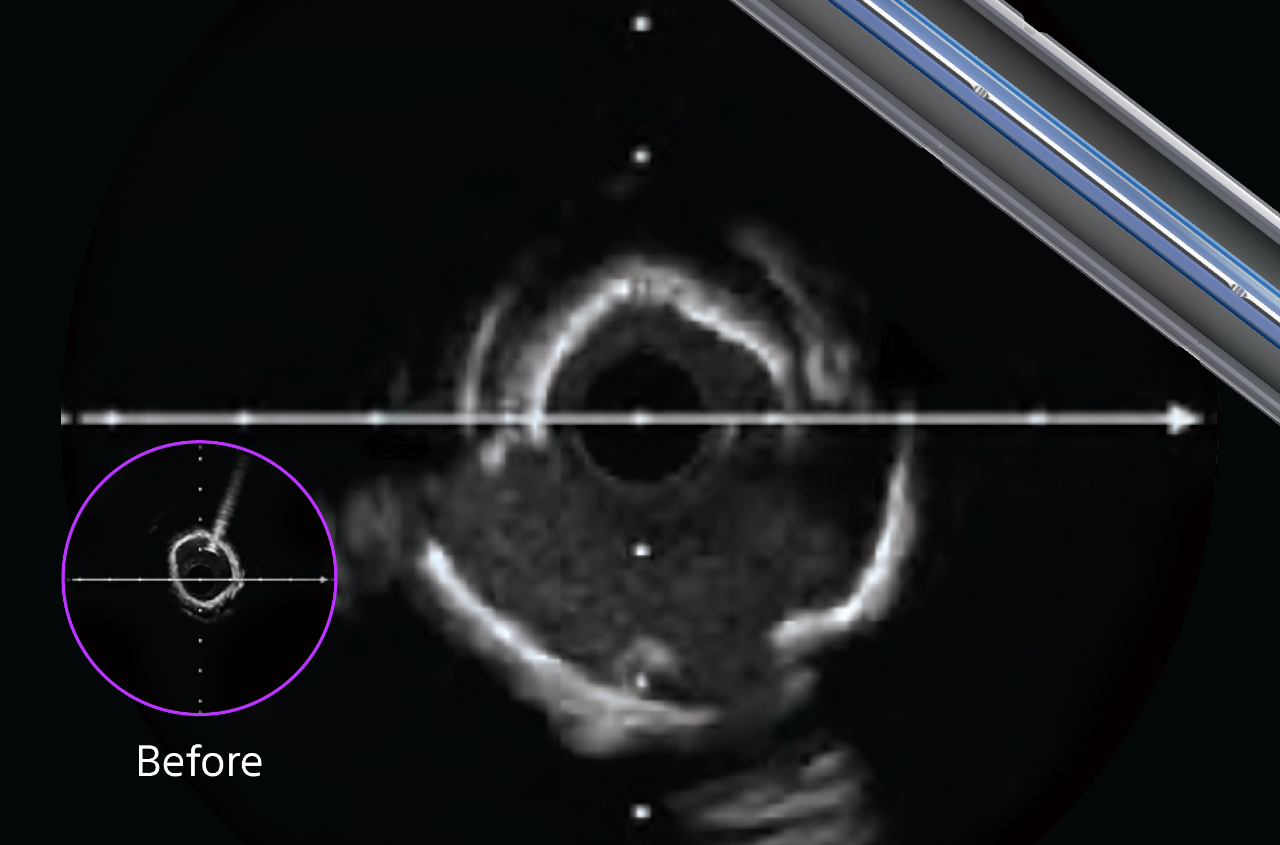
See clearly to prep precisely
Using HD IVUS in every case allows for precise visualization, aiding in faster healing, better procedural efficiency, and stronger long-term outcomes.
Key lesion features:
The ability to identify key lesion features is a critical component of your imaging and treatment decision-making process. By understanding these depth, arc, and thickness characteristics, you can leverage HD-IVUS findings to guide treatment decisions for optimal patient outcomes.




To learn more, visit IVUS 123 Essentials, a step-by-step guide to interpret images and simplify IVUS workflow.
Tips for ISR prep before drug-coated balloon (DCB) treatment
Before proceeding with a DCB treatment for ISR lesions, ensure success by asking yourself these crucial questions:
- Neointimal modification: Has the neointimal tissue been adequately addressed? (Figure A)
- Calcium modification: Is the calcium burden appropriately modified? (Figure B)

Confidently proceed with DCB delivery when these criteria are met:
- Angiography: Ideally, less than 30% residual stenosis should be observed
- Flow: No significant flow-limiting dissection should be present on angiography
- Intravascular imaging: Adequate lumen area is confirmed using IVUS or OCT (goal: minimum stent area ≥ 80% of the distal reference)
Have the right tools for lesion-centric prep
Do you need to crack, cut, debulk, or abate? You must match method to morphology. How a prep therapy interacts with a lesion directly influences the efficacy and safety of the procedure. Prep toolkits must include a variety of tools to consistently facilitate optimal stent deployment on a case-by-case basis.
Continue learning
1. Kheifets, M et al. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jun 24.
2. Généreux, P. et al. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014 May;63(18):1845-1854.
3. Dehmer WJ, et al. Circulation. 2010 Jun 14;121(23):2547-55.
4. Gilutz H, et al. Cathet Cardiovasc Intervent. 2000;50:212-214.
5. Moussa I, et al. Circulation. 1997;96(1):128-136.
6. Nakano M, et al. Eur Heart J. 2013 Jul 3.
7. Adapted from Calcium Algorithm presented by Simon Walsh, MD, Boston.
Case study results are not predictive of results in other cases. Results in other cases may vary.
Photography courtesy of device manufacturers. All trademarks are property of their respective owners.