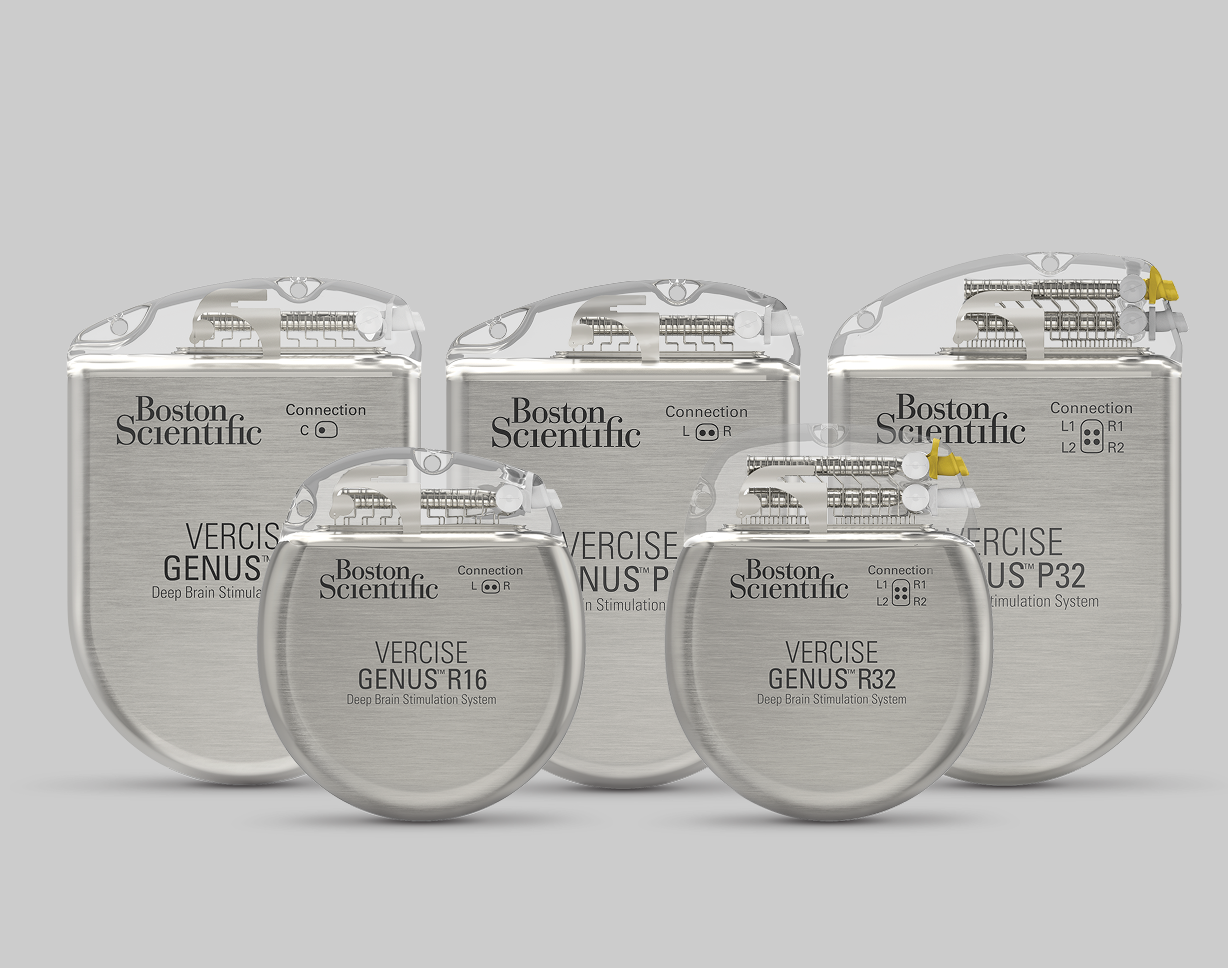
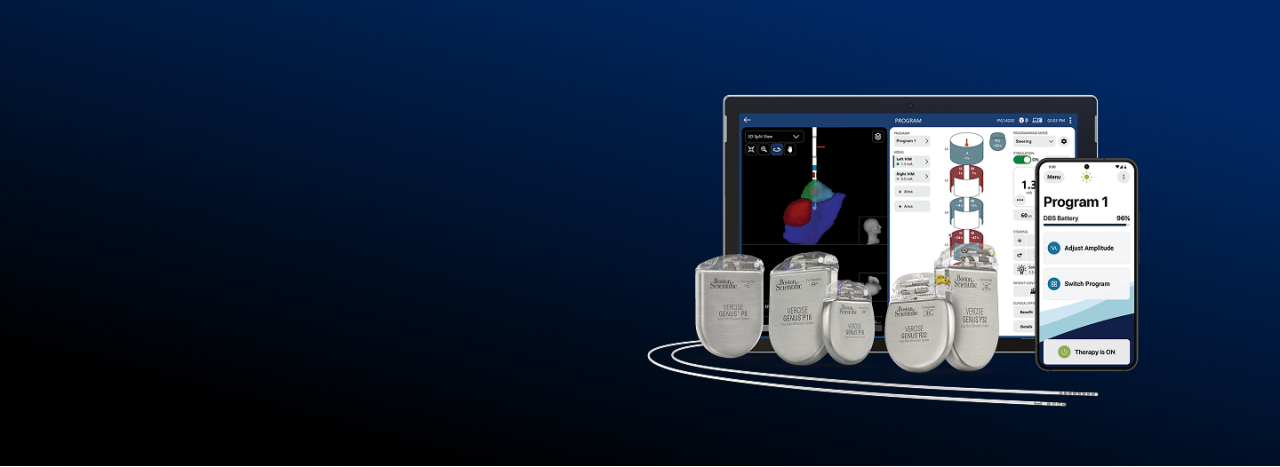
*Information for competitive devices excerpted from the literature published by Medtronic (M982261A015 Rev A, M939241A051 Rev A, M013074C001 Rev B, M982097A013 Rev A, M13075C001 Rev B, M019192C002 Rev A) and Abbott (ARTEN600150429 - B, ARTEN600102238 - A, ARTEN600266398 -A, ARTEN600308953 -A, ARTEN600308947 -A), and Schüpbach, Michael & Chabardes, Stephan & Matthies, Cordula & Pollo, Claudio & Steigerwald, Frank & Timmermann, Lars & Vandewalle, Veerle & Volkmann, Jens & Schuurman, P.. (2017). Directional leads for deep brain stimulation: Opportunities and challenges. Movement Disorders. 32. 10.1002/mds.27096. Steffen, J. K., Reker, P., Mennicken, F. K., Dembek, T. A., Dafsari, H. S., Fink, G. R., Visser-Vandewalle, V., & Barbe, M. T. (2020). Bipolar Directional Deep Brain Stimulation in Essential and Parkinsonian Tremor. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface, 23(4), 543–549. DOI: 10.1111/ner.13109 Reker, P., Dembek, T. A., Becker, J., Visser-Vandewalle, V., & Timmermann, L. (2016). Directional deep brain stimulation: A case of avoiding dysarthria with bipolar directional current steering. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 31, 156-158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.08.007 Kirsch, A. D., Hassin-Baer, S., Matthies, C., Volkmann, J., & Steigerwald, F. (2018). Anodic versus cathodic neurostimulation of the subthalamic nucleus: A randomized-controlled study of acute clinical effects. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders, 55, 61-67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.05.015. Boston Scientific (Vercise ™ Neural Navigator 5 Software Programming Manual MP92736308-01)
**MR-Conditional when all conditions of use are met.
- Torres V, et al. Image-guided programming deep brain stimulation improves clinical outcomes in patients with Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024 Jan 27;10(1):29.
- Image Guided programming in PD patients enables a reduction in programming time compared with standard clinical based programming (p=39). Lange F, Et al. Reduced Programming Time and Strong Symptom Control Even in Chronic Course Through Imaging-Based DBS Programming. Front Neurol. 2021 Nov 8;12:785529. N=10
- Lange F, et al. (2021). Reduced Programming Time and Strong Symptom Control Even in Chronic Course Through Imaging-Based DBS Programming. Front. Neurol. 12:785529. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.785529
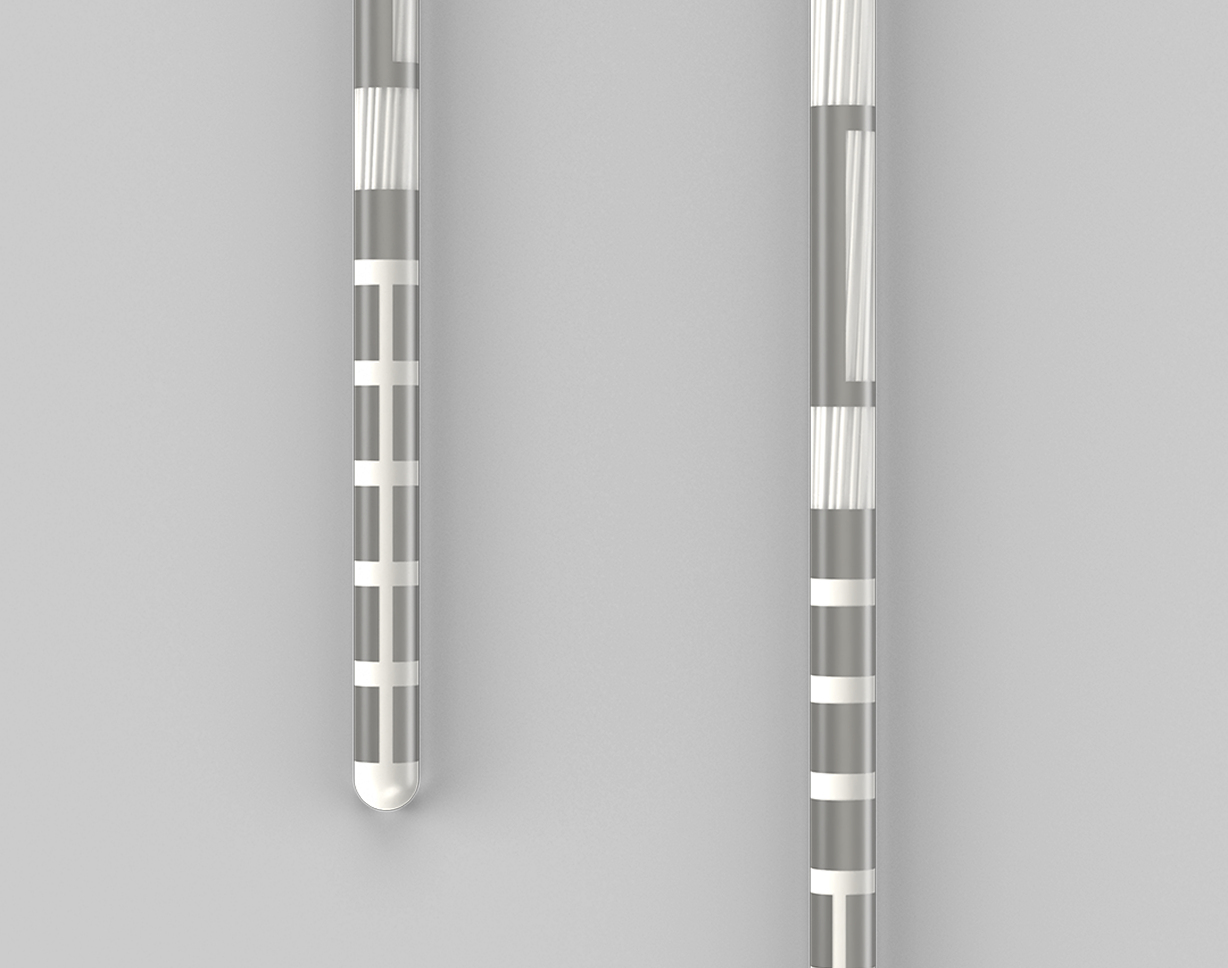
- Best is defined as the directional lead with the longest directional span and most directional levels Boston Scientific. (2024). Vercise™ Deep Brain Stimulation Systems Surgical Implant Manual. Medtronic. (2021). Medtronic Sensight™ Directional Lead Kit.https://www.medtronic.com/content/dam/emanuals/neuro/M982098A_a_013_view.pdf Abbott. (2021). Lead and Extensions Kits for Deep Brain Stimulation Systems. Clinician’s Manual.https://manuals.eifu.abbott/en/detail-screen.htm
- Reker P, Dembek TA, Becker J, Visser-Vandewalle V, Timmermann L. Directional deep brain stimulation: A case of avoiding dysarthria with bipolar directional current steering. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016 Oct:31:156–158.
- Kirsch AD, Hassin-Baer S, Matthies C, Volkmann J, Steigerwald F. Anodic versus cathodic neurostimulation of the subthalamic nucleus: A randomized-controlled study of acute clinical effects. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2018 Oct:55:61-67.
- Yu et al. (2013). “Characterizing Rechargeable IPG Charge Cycle Time in DBS.” NANS 2013 Poster.