Urology and Pelvic Health

Delivering Meaningful Innovation
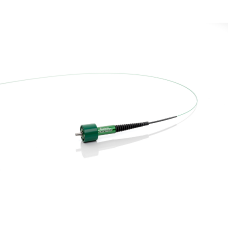
Changing the Scope Market. The LithoVue™ Single-Use Digital Flexible Ureteroscope delivers detailed high-resolution digital images for high-quality visualization and seamless navigation—to help urologists remove kidney stones efficiently and affordably. By eliminating the operational inefficiencies and cost of reusable ureteroscopes, the LithoVue™ System is changing the way our customers think about flexible ureteroscopy.
Expanding Options for Addressing Men's Health. The Rezūm® System complements our existing offerings for the treatment of symptomatic BPH, providing our customers with options to treat patients at every stage of the BPH journey. Additional solutions in the portfolio to treat BPH include the Greenlight XPSTM Laser Therapy system and holmium platforms.
Conditions We Treat
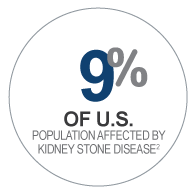
- Kidney Stones
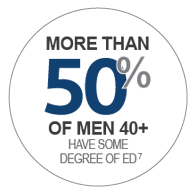
- Erectile Dysfunction
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
- Male Incontinence
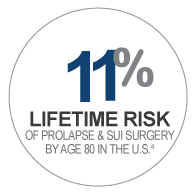
- Pelvic Floor Disorders (Stress Urinary Incontinence and Pelvic Organ Prolapse)
- Heavy Menstrual Bleeding (Menorrhagia)
- Uterine Fibroids
Solutions We Offer
- Stone Management
- BPH Management
- Penile Implants for Erectile Dysfunction
- Urinary Control Systems for Male Stress Urinary Incontinence
- Mid-Urethral Sling for Female Stress Urinary Incontinence
- Pelvic Floor Reconstruction
- Endometrial Ablation and Uterine Fibroid Removal

Patient Impact



Sources
* Data on file at Boston Scientific. For patients who undergo surgical therapy for ED.
1. Data on file at Boston Scientific.
2. Scales, Charles D., et. al. Prevalence of Kidney Stones in the United States. European Urology, 62 (2012), p 160-165.
3. American Journal of Managed Care. 2006 Apr; 12 (5 Suppl): S122-8.
4. Olsen AL, Smith VJ, Bergstrom JO, Colling JC, Clark AL (1997) Epidemiology of surgically managed pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence. Obstet Gynecol 89(4):501-506.
5. Kaunitz, Andrew. Approach to abnormal uterine bleeding in non-pregnant reproductive age women, www.uptodate.com, 2015.
6. Irwin C, Kopp Z, Agatep B, Milsom I, Abrams P. Worldwide prevalence estimates of lower urinary tract symptoms, overactive bladder, urinary incontinence and bladder outlet obstruction. BJU Int. 2011;108:1134.
7. Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, et al. Impotence and its medical and psychosocial results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol. 1994 Jan;151(1):54-61.
8. Ovarian Cancer Research Fund Alliance. Statistics on ovarian cancer. https://ocrfa.org/patients/about-ovarian-cancer/statistics/. Accessed June 25, 2018.