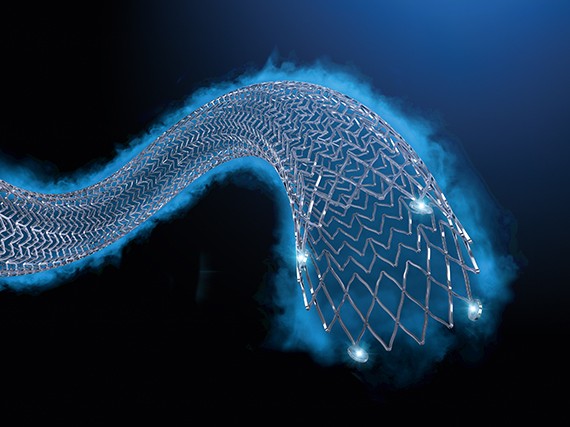
Choose the right DET to give patient the most durable outcomes
More evidence.
The only drug-eluting technologies (DET) for use in the superficial femoral artery (SFA) backed by 6 Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs), and studies that will exceed 10,000 patients1,6.
More confidence.
Consistent outcomes in RCTs and real world studies give you the confidence to choose EluviaTM and RangerTM DET.7-8
More successful outcomes.
Fewer repeat procedures with Eluvia and Ranger compared to alternative devices.9-10
Our commitment to addressing restenosis
Doctors around the world rely on Ranger™ Drug-coated Balloon (DCB) and Eluvia™ Drug-Eluting Stent (DES) to give their patients the very best chance of achieving and maintaining patency in the superficial femoral artery, confident in the knowledge they have been rigorously studied in both controlled and real-world settings.
Both products leverage the proven safety and efficacy of paclitaxel to inhibit restenosis, delivered via innovative next-generation platforms. The numbers speak for themselves.9
Restenosis after SFA Interventions remains highly prevalent
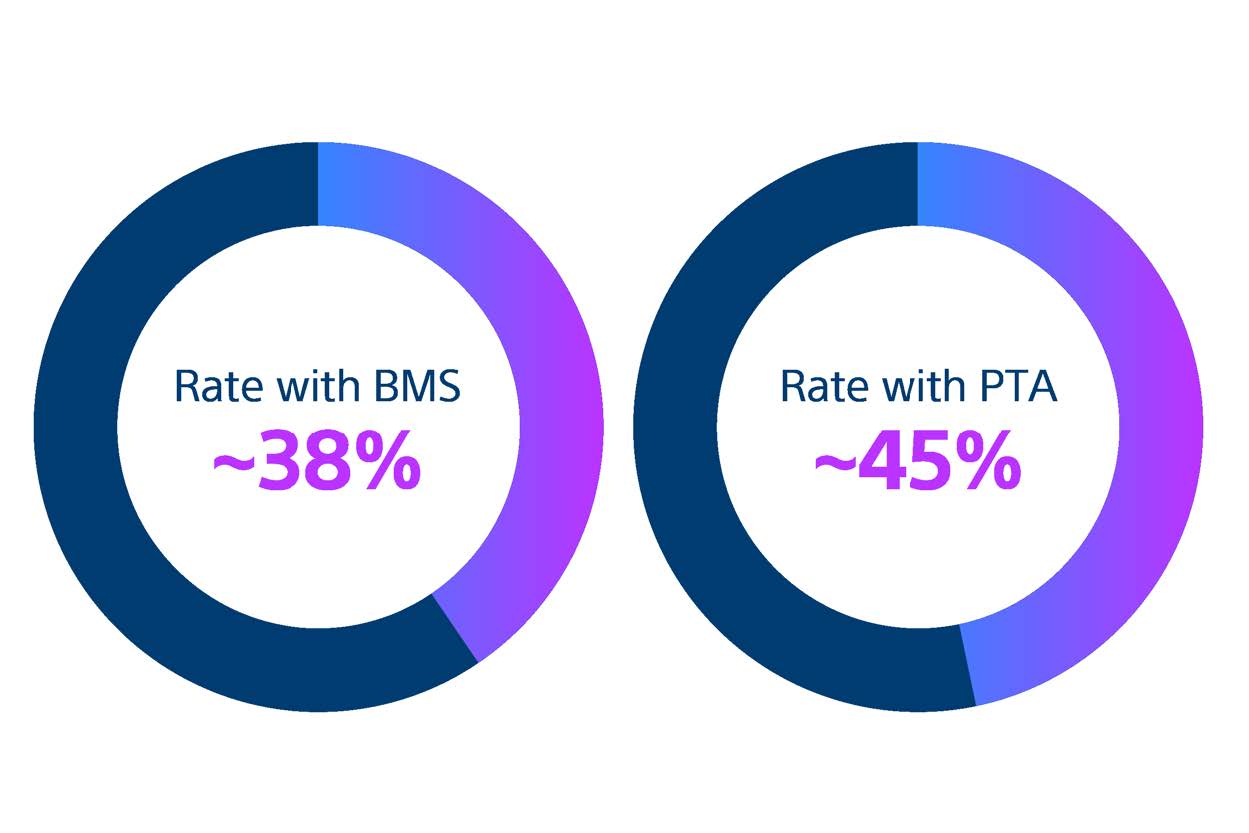
Bare metal stents (BMS) and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) are still widely used despite being associated with high restenosis rates.9
Since the first use of PTA nearly 60 years ago, SFA disease management remains inconsistent. BMS and PTA are still widely used even though meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials reveal that they are associated with high restenosis rates.9-10
New-generation endovascular approaches, however, such as drug coated devices, have helped to reduce restenosis rates.2,11
More evidence. More confidence.
Eluvia and Ranger are defining a new standard of care in SFA treatment with robust clinical data1-8,12-25
More successful outcomes for your patients
Drug-Eluting Technologies
References
1. Sachar R et al. RANGER II SFA Investigators. 1-year results from the RANGER II SFA randomized trial of the Ranger drug-coated balloon. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2021;10:1123–1133.
2. Gouëffic Y, et al. Efficacy of a drug-eluting stent versus bare metal stents for symptomatic femoropopliteal peripheral artery disease: Primary results of the EMINENT randomized trial. Circulation. 2022;146:1564–1576.
3. Steiner S, et al. 12-month results from the first-in-human randomized study of the ranger paclitaxel-coated balloon for femoropopliteal treatment. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;11:934–941.
4. Steiner S, et al. COMPARE: prospective, randomized, non-inferiority trial of high- vs. low-dose paclitaxel drug-coated balloons for femoropopliteal interventions. Eur Heart J. 2020;41:2541–2552.
5. Müller-Hülsbeck S, et al. Two-year efficacy and safety results from the IMPERIAL Randomized study of the Eluvia polymer-coated drug-eluting stent and the Zilver PTX polymer-free drug-coated stent. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2021;44:368–375.
6. Marianne Brodmann, CIRSE 2022 Symposium: DET in complexities co-morbidities, and underserved patient populations.
7. Torsello G, Real World Evidence, LINC 2023
8. Iida O, Real World Data from Japan, LINC 2023
9. Kasapis C, et al. Routine stent implantation vs. percutaneous transluminal angioplasty in femoropopliteal artery disease: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur Heart J. 2009;30(1):44–55
10. Aboyans V, et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Arterial Diseases, in collaboration with the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur Heart J. 2018;39:763–816.
11. Ullah W, et al. Safety and efficacy of drug-coated balloon for peripheral artery revascularization-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2022;99(4):1319–1326.
12. Randomised Controlled Trials: Brodmann M. Randomised Control Trial Data: The Pinnacle of Proof. Presented at LINC 2023, Leipzig, Germany, 6–9 June 2023.
13. Popcorn Type R: Imada K. POPCORN Type R. JET 2023, May 26, 2023, Tokyo.
14. Popcorn 2Y: Tanaka A. POPCORN 2Y Result. JET 2023, May 26, 2023, Tokyo
15. Capsicum: Iida O, Takahara M, Soga Y, et al; CAPSICUM Investigators. 1-Year Outcomes of Fluoropolymer-Based Drug-Eluting Stent in Femoropopliteal Practice: Predictors of Restenosis and Aneurysmal Degeneration. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2022 Mar 28;15(6):630–638. Iida LINC 2023.
16. Muenster 5yrs: Torsello G. LINC 2023; June 6, 2023; Leipzig, Germany.
17. Desafinado: Kum S, Ipema J, Huizing E, et al. Outcomes of the paclitaxel-eluting Eluvia stent for long femoropopliteal lesions in Asian patients with predominantly chronic limb-threatening ischemia. Vasc Med. 2021;26(3):267–272.
18. Regal: Lansik W. Real world all-comers data from the REGAL registry – 2-year results. Presented at LINC 2023.
19. Auckland: Holden, A. Single Centre Long-Term Experience with the Boston Scientific Eluvia DES in Femoro-popliteal Artery Occlusive Disease. Presented at LINC 2020.
20. Capricorn: Soga Y, JET 2023.
21. Prospect-Monster: Nakama, T. Second-generation low-dose drug-coated balloon vs high-dose drug-coated balloon for symptomatic femoropopliteal artery disease: The result from the PROSPECT-MONSTER study. Presented at LINC 2023.
22. K-ELUVIA: Ko YG. 2-year clinical outcome of the Eluvia drug-eluting stent for femoropopliteal lesions: A prospective multicenter K-ELUVIA registry. Presented at LINC 2023
23. Ranger China: Prospective, Non-randomized, Multicentre Clinical Study of the Boston Scientific Paclitaxel-Coated PTA Balloon Catheter (Ranger™ and Ranger™ SL (OTW) DCB) in China: NCT02944971 Zhong Chen, dr.,Beijing Anzehn hospital July 2023.
24. Ranger SFA Registry: Prospective Multicentre all-comer registry Lichtenberg M. CIRSE 2017, BSC Symposium Study is sponsored by Klinikum Arnsberg.
25. SPORTS: Tepe G. SPORTS. TCT 2023, October 24, 2023, San Francisco, CA.
26. EMINENT Trial: A global randomized controlled multi-center trial with 2:1 randomization of the Eluvia™ Drug-Eluting Stent against commercially-available Self-Expanding Bare Nitinol Stents, single-blind, superiority design; independent core lab adjudication. Primary Endpoint: 1-Year Binary Primary Patency rate of 83.2% in the Eluvia arm vs. 74.3% in the Bare-Metal Stenting arm (p-value = 0.0077).
27. Boston Scientific Data on File. Ranger Catheter Competitive Testing Report, 92517674. Measurements taken from 6 x 120 devices for Ranger DCB, Lutonix™ 035 DCB, IN.PACT Admiral DCB and Stellarex™ 035 DCB. Lutonix 018 DCB measurements taken from 6 x 150 devices.
28. RANGER II SFA RCT 2-Year Results presented by Ravish Sachar, MD. VIVA 2021.
Caution:
The law restricts these devices to sale by or on the order of a physician. Indications, contraindications, warnings, and instructions for use can be found in the product labelling supplied with each device or at www.IFU-BSCI.com. Products shown for INFORMATION purposes only and may not be approved or for sale in certain countries. This material not intended for use in France.