WHAT IS STROKE?
Stroke is a medical emergency, a brain attack – the brain equivalent of a heart attack.
A stroke happens when blood flow to the brain is reduced or blocked. Without the oxygen-rich blood and nutrients your brain cells need to thrive, they start to die and can cause brain damage.
Every year around 17 million people suffer a stroke worldwide. It is estimated that 1 in 4 people will have a stroke during their lifetime. Although stroke can affect anyone at any time, two-thirds of all strokes occur in people aged over 65 years. The number of people living with stroke is estimated to increase by 27% between 2017 and 2047 in the European Union, mainly because of population ageing and improved survival rate but not only. Innovative medical solutions can save lives and significantly improve quality of life, but like all medical procedures, it may involve risk.
At Boston Scientific we are committed to prevent Stroke risk, learn more here on this page.
Learn from the experts, discussing about stroke risk prevention on the World Stroke Day
- Prof. Ole de Backer, Interventional Cardiologist, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen Denmark
- Dr. Fabrizio Pennacchi, President of ALICe Italy

STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE
What Is Severe Aortic Stenosis?
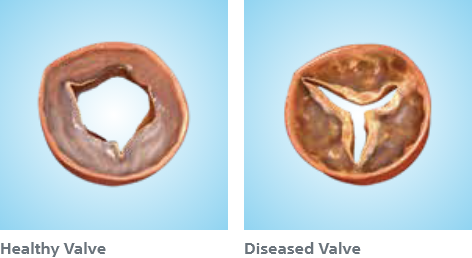
Severe aortic stenosis occurs when the aortic valve leaflets becomes stiff, reducing their flexibility and ability to fully open and close properly.
This results in a narrowing (stenosis) of the valve opening. This narrowing reduces and restricts blood flow, requiring your heart to work harder.

STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE
Severe Aortic Stenosis Pathology & Symptoms
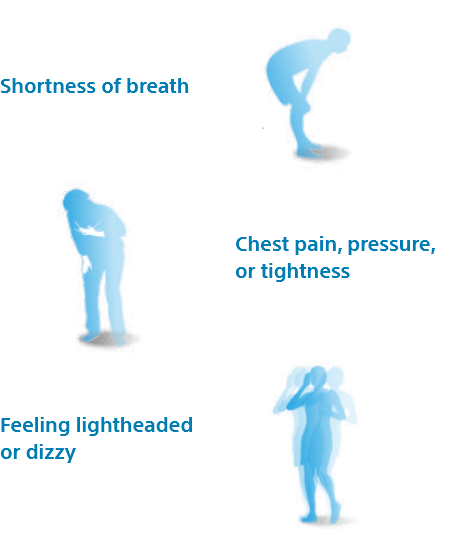
This narrowing reduces and restrict blood flow, requiring your heart to work harder. As a result, less oxygen-rich blood flows from your lungs to the brain and the rest of your body.
Atrial Fibrillation Pathology & Symptoms
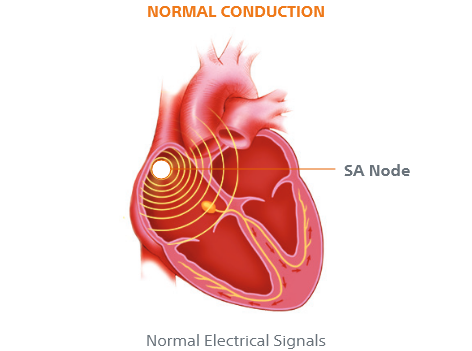
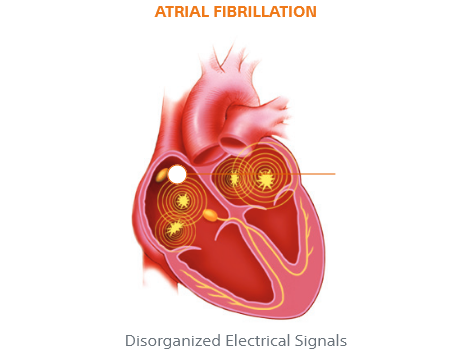
In a healthy beating heart, your blood pumps in a steady, coordinated fashion in the chambers of your heart to and from other parts of your body. Atrial fibrillation (AFib) happens when the top two chambers of the heart, the atria, beat too fast and with an irregular rhythm (fibrillation).

FROM PATHOLOGY TO TREATMENT OPTIONS
TAVI and the associated risk of Stroke
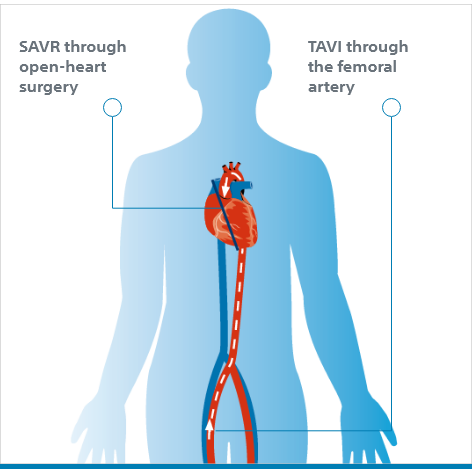
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) is a less invasive procedure that replaces the diseased aortic valve without opening your chest to reach your heart. TAVI can save lives and significantly improve quality of life, but like all medical procedures, it may involve risk.
Atrial Fibrillation and the associated risk of Stroke
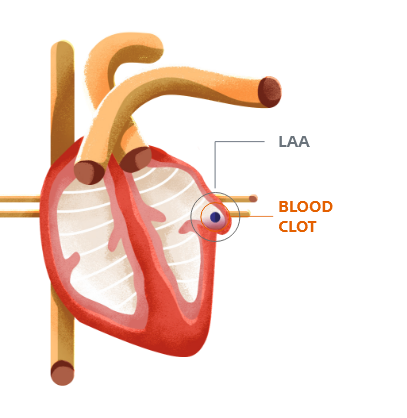
That’s because AF causes your heart to beat irregularly, which affects its ability to pump blood normally and when the heart doesn’t pump as it should, blood can collect and form clots.
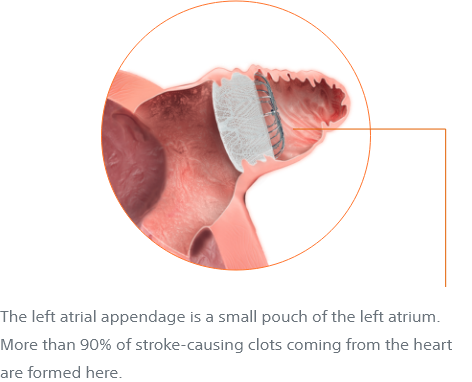
1. AF causes blood to stagnate in the left atrial appendage (LAA)
2. The stagnant blood becomes an ideal environment for athrombus or blood clot to form
3. The blood clot, or portion of it, dislodges from the LAA and travels through the arterial system
4. The embolism lodges itself in the blood vessels of the brain, restricting blood flow and causing a stroke
STROKE RISK REDUCTION IS POSSIBLE
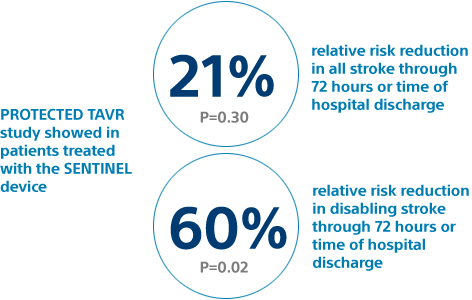
Stroke is a Devasting Event Minimize the risk of stroke during your TAVR procedure
All stroke occurs on average 4% of the time
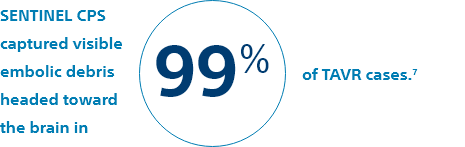
During the aortic valve replacement procedure, pieces of the calcified heart valve, or other debris, can break loose and travel through the arteries toward the brain. This material is called embolic debris. If left unaddressed, the debris could cause blockages, potentially leading to stroke.

TREATMENT OPTIONS
How the SENTINEL™ Cerebral Protection System Works
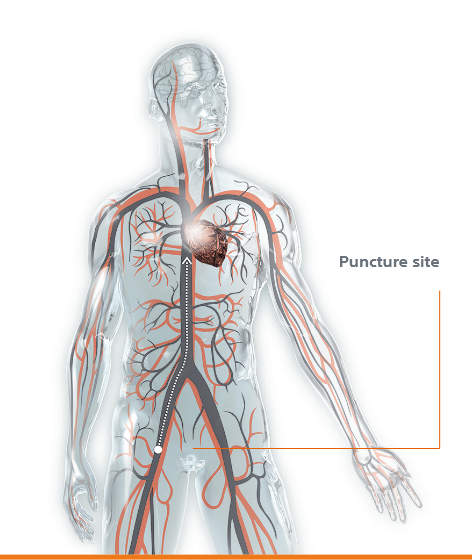
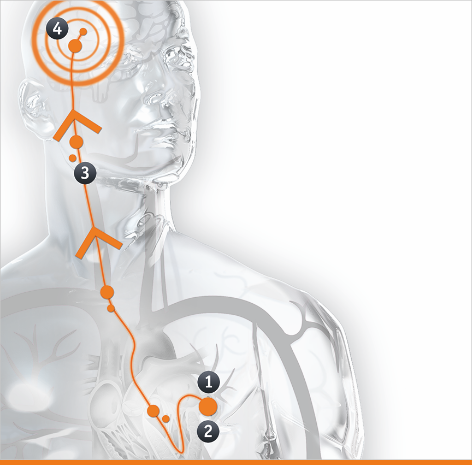
1. The SENTINEL device is placed at the beginning of the TAVR procedure through a small puncture in the right wrist.
2. Two tiny filters are placed in the main arteries that carry 90% of the blood to the brain. These filters collect any dislodged debris, preventing it from traveling to the brain.
3. At the completion of the TAVR procedure, the filters and collected debris are removed from the body.
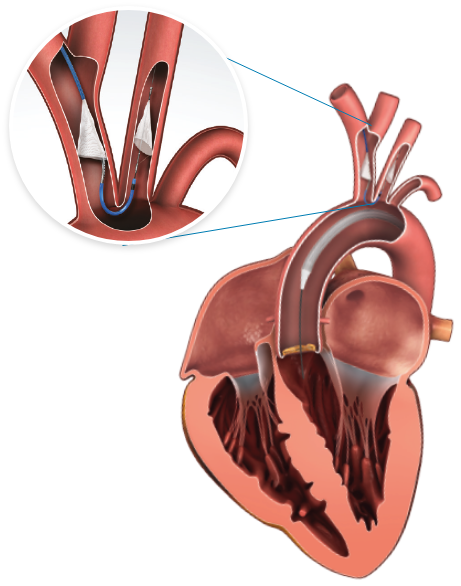


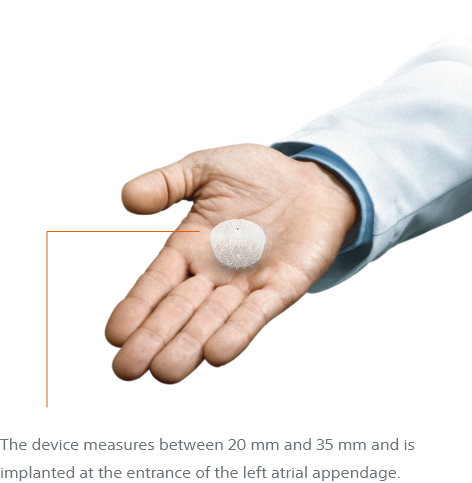
What is the WATCHMAN FLX™ LAA Closure device?
The WATCHMAN FLX™ device is a permanent implant designed to keep harmful blood clots from entering your blood stream, potentially causing a stroke. It is made from very light and compact materials commonly used in many other medical devices.