1.Estimates shown are based on geometric calculations and averagecell size; actual tumor cell counts may vary. Wee JJ, Tee CL,Junnarkar SP, et al. Outcomes of surgical resection of super-giant (≥15cm) hepatocellular carcinoma: Volume does matter, if not the size. JClin Transl Res. 2022;8(3):209-217. Published 2022 May 25.
2.Arzumanian VA, Kiseleva OI, Poverennaya EV. The Curious Case of theHepG2 Cell Line: 40 Years of Expertise. Int J Mol Sci.2021;22(23):13135. Published 2021 Dec 4.doi:10.3390/ijms222313135
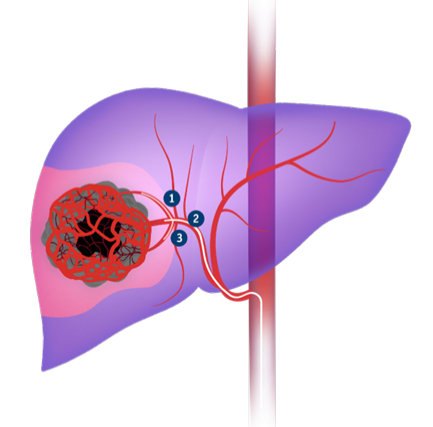
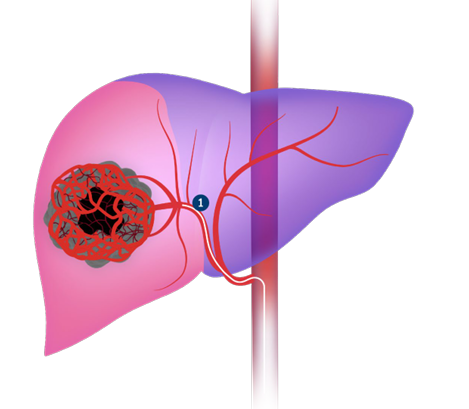
3.Pellerin O, Lin M, Bhagat N, et al. Can C-arm cone-beam CT detect a micro-embolic effect after TheraSphere radioembolization of neuroendocrine and carcinoid liver metastasis? Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2013;28(6):459–65.
4.Atassi B, Bangash AK, Bahrani A, et al. Multimodality imaging following 90Y radioembolization: A comprehensive review and pictorial essay. Radiographics. 2008;28(1):81–99.
5.Young S., Chen T, Flanagan S, et al. Realized tumor to normal ratios in hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing transarterial radioembolization: A retrospective evaluation. Eur Radiol. 2022;32:4160-7.
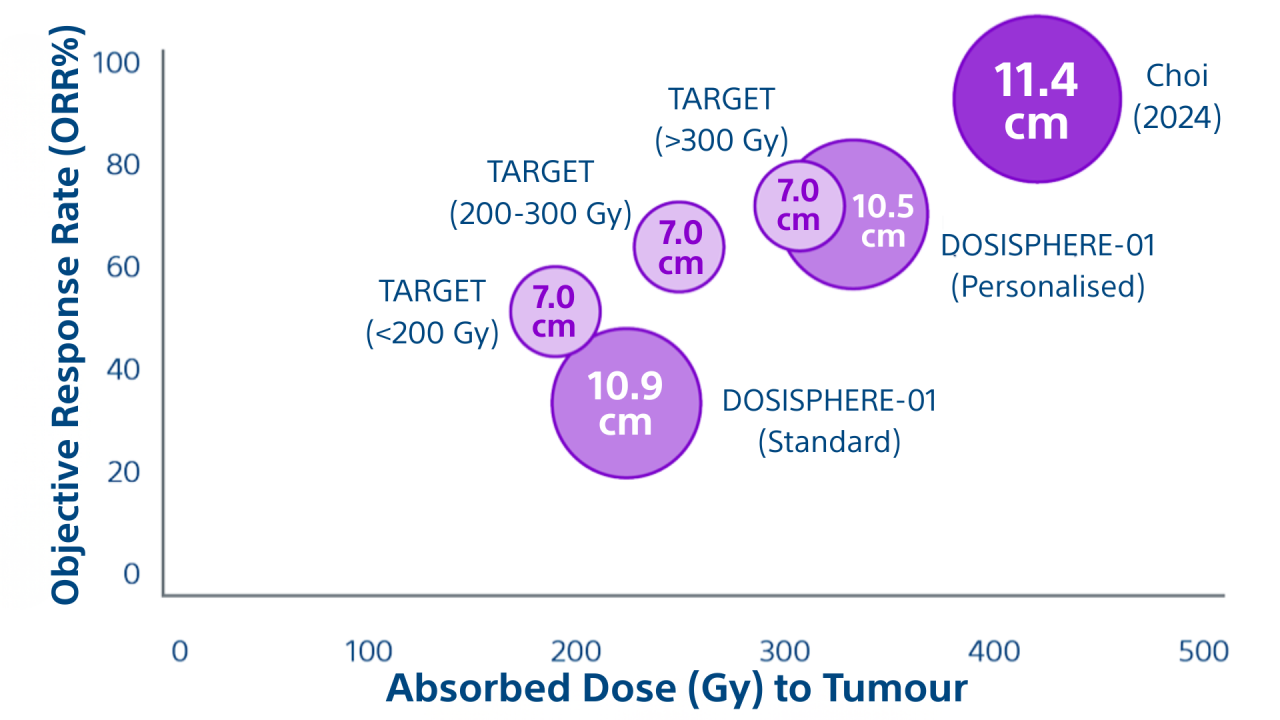
6.Garin E, Tselikas L, Guiu B, Chalaye J et al. Personalised versus standard dosimetry approach of selective internal radiation therapy in patients with locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (DOSISPHERE-01): a randomised, multicentre, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020; Published Online: November 06, 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30290-9
7.Lam, M., Garin, E., Maccauro, M. et al. A global evaluation of advanced dosimetry in transarterial radioembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with Yttrium-90: the TARGET study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-022-05774-0.
8.Choi JW, Suh M, Paeng JC, Kim JH, Kim HC. Radiation Major Hepatectomy Using Ablative Dose Yttrium-90 Radioembolization in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma 5 cm or Larger. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2024 Feb;35(2):203-212.