The SEATTLE II trial is a prospective, single-arm, multicentre trial of ultrasound-facilitated, low-dose fibrinolysis for acute massive and submassive pulmonary embolism. It run in 2015 and consolidated RV/LV results.
G. Piazza MD, MS et al, JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015 Aug 24; 8(10): 1382-92
Clinical significance
Trial overview
- Prospective, multi-center, single-arm trial
- 150 patients with acute submassive (n=119) and massive (n=31) PE
- 22 centres in the US
- Infusion time: 12 hours. Total dose: 24 mg
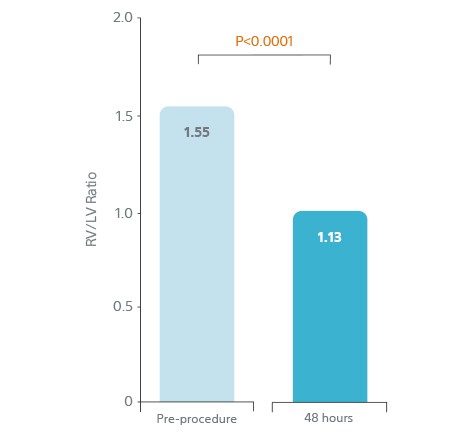
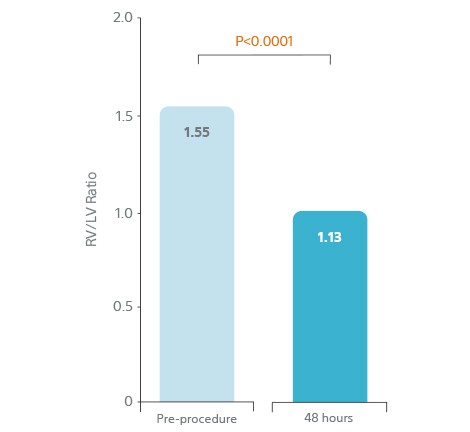
- 25% reduction (p<0.0001) in RV/LV ratio 48 h from baseline
- 6.7 reduction (p<0.0001) in Thrombus Burden 48 h from baseline
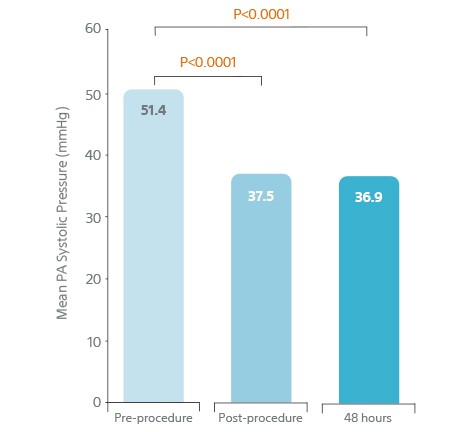
- 13.9 mm Hg reduction (p<0.0001) in PA systolic pressure 48 h from baseline
- GUSTO severe/life-threatening bleed: 0.67%; GUSTO moderate bleed: 9.3%
- 0 ICH
Patients

Key results
- 25% decrease in RV/LV ratio over 48 hours.
- 0 intercranial haemorrhage observed, minimising the risk of this severe event.
- Rapidly relieved pulmonary artery obstruction.
- Reduced pulmonary hypertension.
25% Decrease in RV/LV Ratio
Over 48 Hours
Rapidly Relieved Pulmonary
Artery Obstruction
Minimised Risk of
Intracranial Haemorrhage
Minimised risk of intracranial haemorrhage
Study | Intracranial |
ICOPER (Goldhaber SZ, et al. 1999) | 9/304 (3%) |
PEITHO | 10/506 (2%) |
SEATTLE II | 0/150 (0%) |
Trial conclusions
Ultrasound-facilitated, catheter-directed, low-dose fibrinolysis for acute PE improves RV function and decreases pulmonary hypertension and angiographic obstruction. By minimising the risk of intracranial bleed, it represents a potential “game-changer” in the treatment of high-risk PE patients.
Trial bibliography
2015 - SEATTLE II: A Prospective, Single-Arm, Multicentre Trial of Ultrasound-Facilitated, Low-Dose Fibrinolysis for Acute Massive and Submassive pulmonary embolism
G. Piazza MD, MS et al, JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015 Aug 24; 8(10): 1382-92
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26315743/
Caution:
The law restricts these devices to sale by or on the order of a physician. Indications, contraindications, warnings, and instructions for use can be found in the product labelling supplied with each device or at www.IFU-BSCI.com. Products shown for INFORMATION purposes only and may not be approved or for sale in certain countries. This material not intended for use in France.