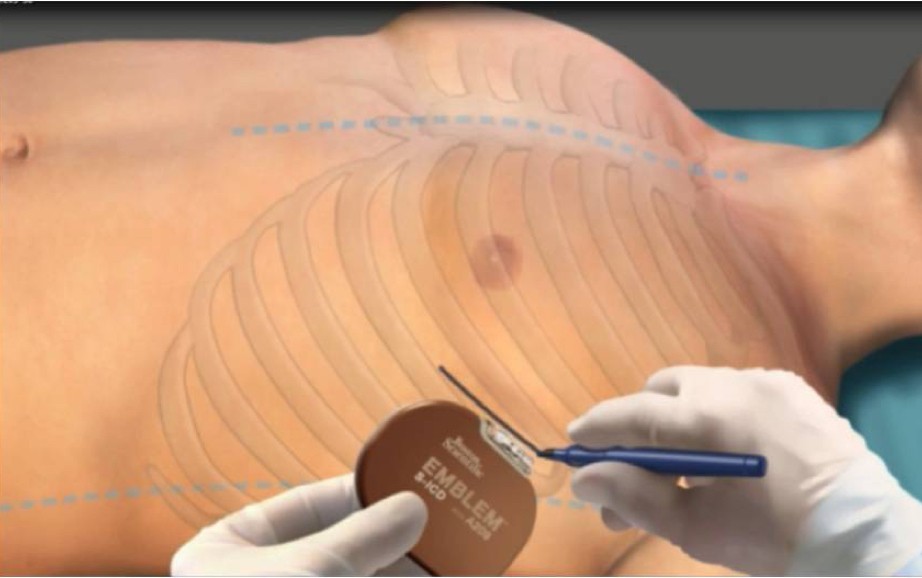
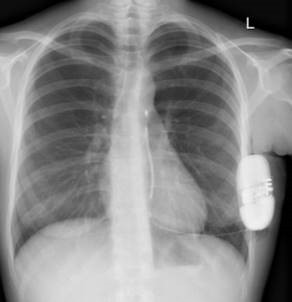
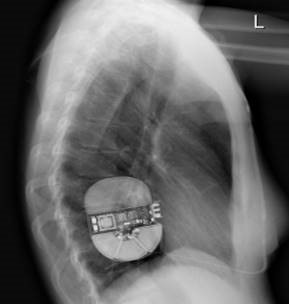
EMBLEM™ MRI S-ICD System
Subcutaneous Implantable Defibrillator
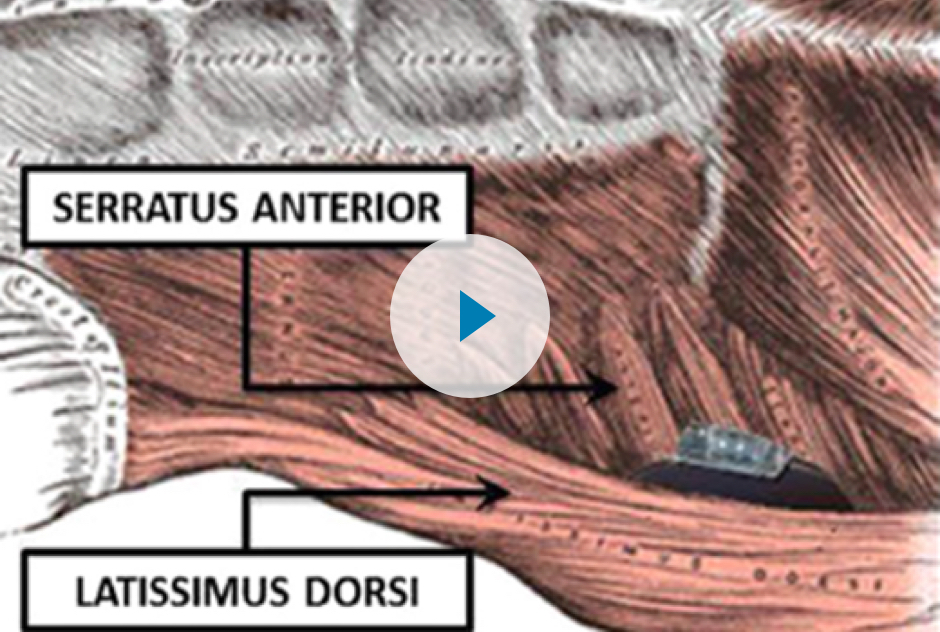
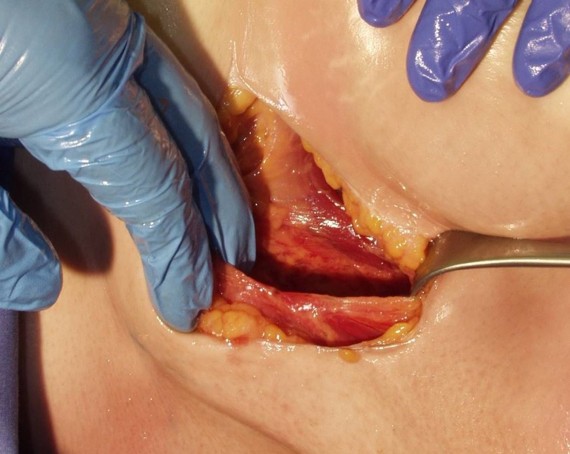
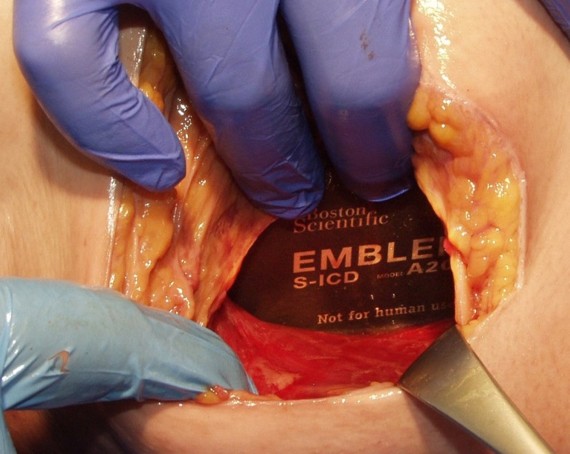
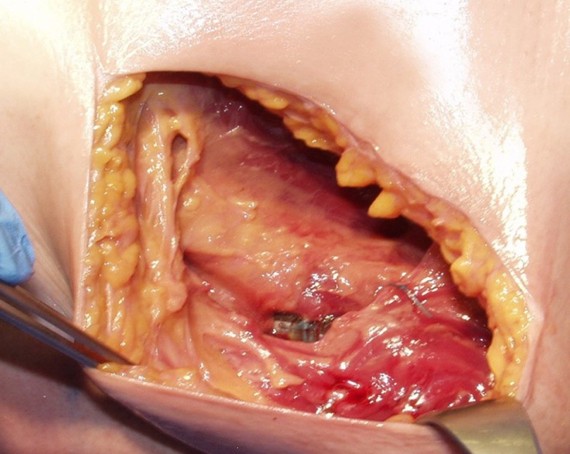
The Intermuscular Technique Has Many Benefits1-6
- Optimal position for DFT and impedance measurements
- Reduced risk of pocket complications (erosion and infection)
- Reduced device migration
- Consistency in implant technique
- Enhanced patient comfort as the device is protected by the muscle layer
- Excellent cosmetic outcomes
- Intermuscular placement can be particularly beneficial in low and high BMI patients
Intermuscular Implant Technique for S-ICD
In this video, Professor Joachim Winter, MD, PhD describes the intermuscular technique for implanting the S-ICD and discusses patient considerations and the clinical and cosmetic benefits of the technique.
2-Incision Implant Technique
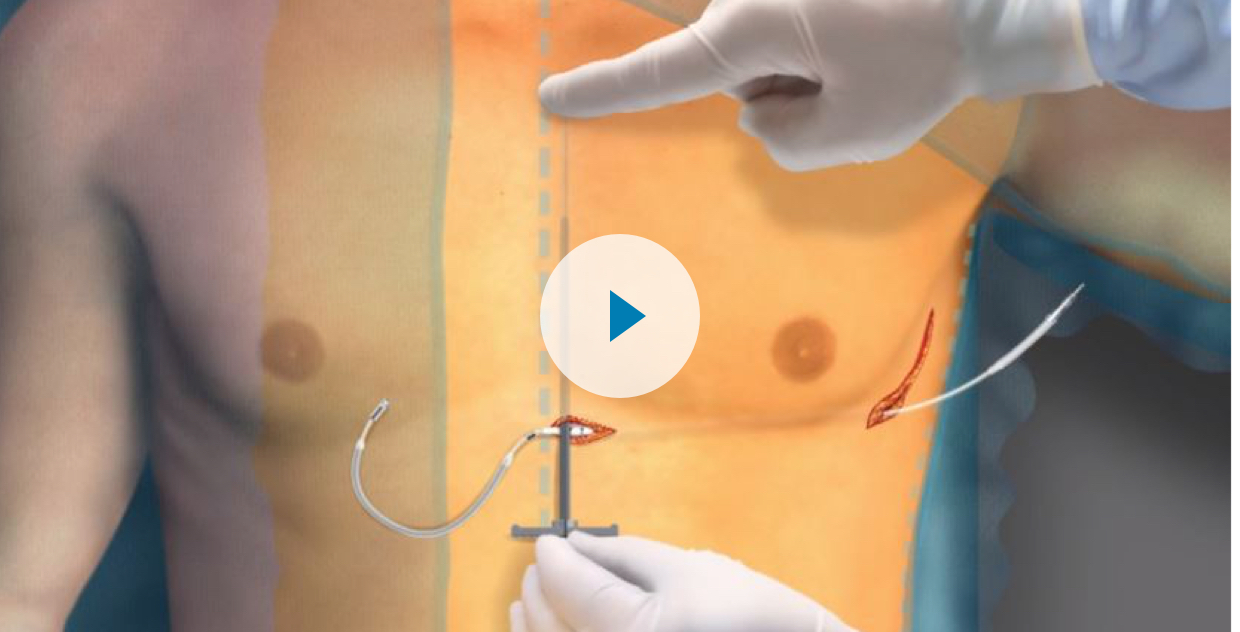
Procedure Animation
By eliminating the superior parasternal incision used in the three-incision technique, the two-incision implant technique reduces procedure time and improves cosmetic outcomes.7,8
Training & Education

Explore continuing education courses, best practices modules and other training and resources for S-ICD.
Why S-ICD?
See how S-ICD helps protect patients at risk for sudden cardiac death while also eliminating the risk of TV-ICD lead complications.

References
1. Winter, J. et al. Submuscular is Superior to Subcutaneous Implantation for Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator. Circulation. 2013;128:A14688.
2. Winter, J. et al. Intermuscular technique for implantation of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator: long-term performance and complications. Europace. 2016
3. Ferrari, P. et al. Intermuscular pocket for subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator: single-centre experience. Journal of Arrhythmia. 2016; 32, 223–226.
4. Droghetti, A. et al. Totally submuscular implantation of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator: a safe and effective solution for obese or oversized patients. Clinical Case Reports. 2016
5. Kondo, Y. et al. Successful intermuscular implantation of subcutaneous implantable cardioverter defibrillator in a Japanese patient with pectus excavatum. Journal of Arrhythmia. 2016
6. Migliore, F. et al. Intermuscular Two-Incision Technique for Subcutaneous Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator Implantation: Results from a Multicenter Registry. Pace. 2016
7. Brouwer TF, Miller MA, Quast ABE, Palaniswamy C, Dukkipati SR, Reddy V, Wilde AA, Willner JM, Knops RE. Implantation of the subcutaneous implantable cardioverter-defibrillator: an evaluation of 4 implantation techniques. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2017; 10:e004663. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.116.004663.
8. Knops RE, Olde Nordkamp LR, de Groot JR, Wilde AA. Two-incision technique for implantation of the subcutaneous implantable cardio-verter-defibrillator. Heart Rhythm. 2013; 10:1240-1243. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2013.05.016.