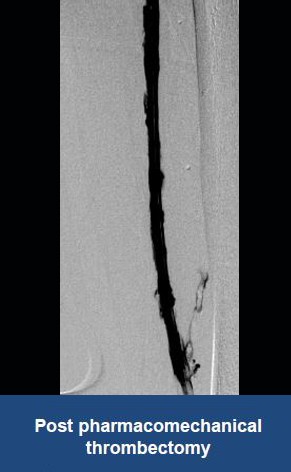
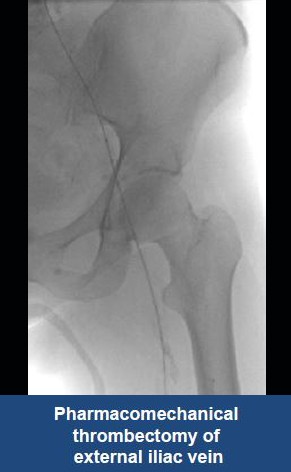
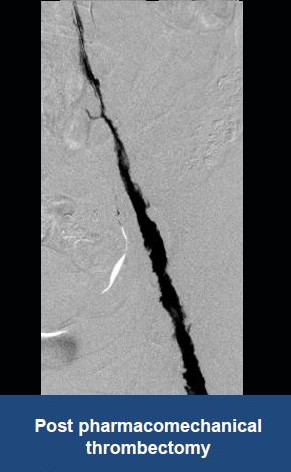
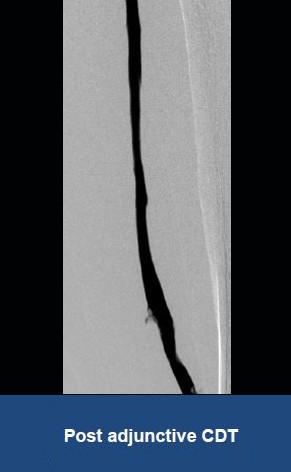
AngioJet™
Ultra Thrombectomy System
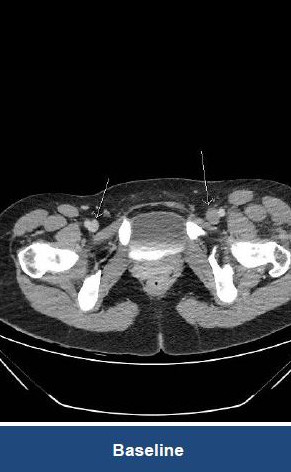
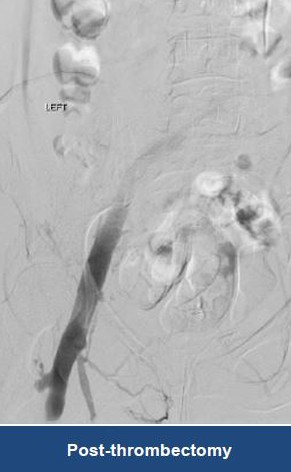
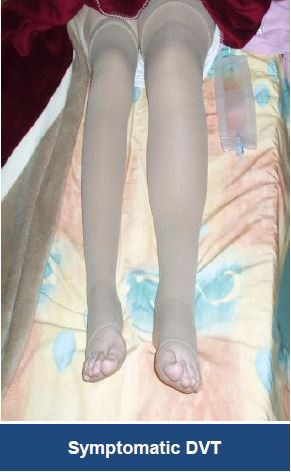
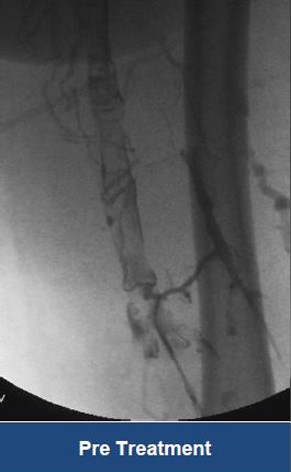
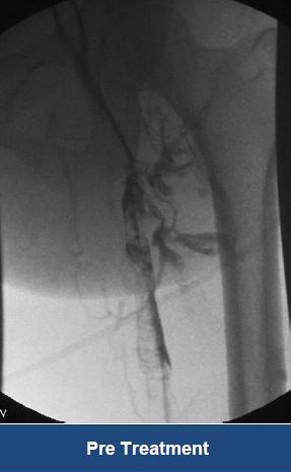
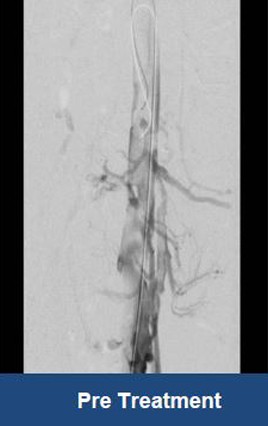
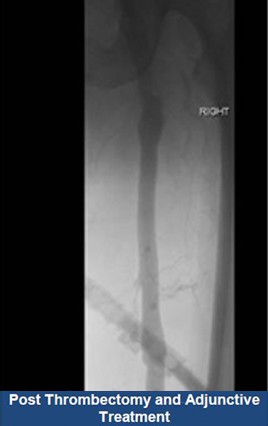
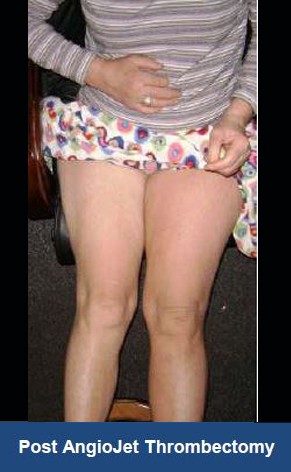
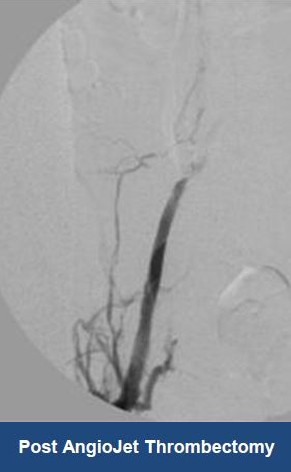
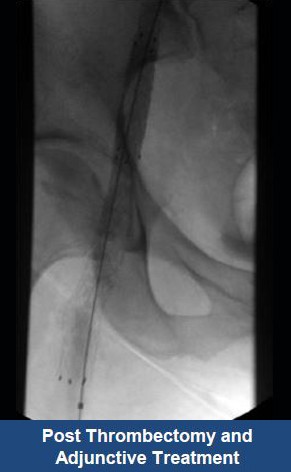
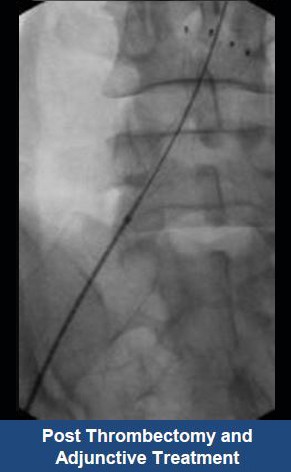
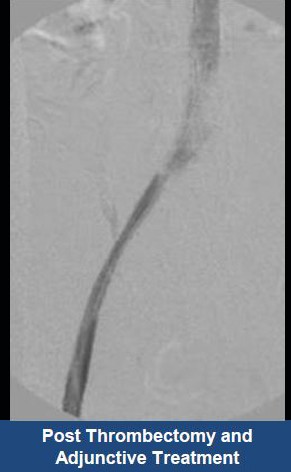
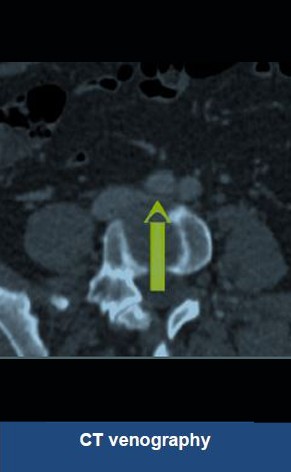
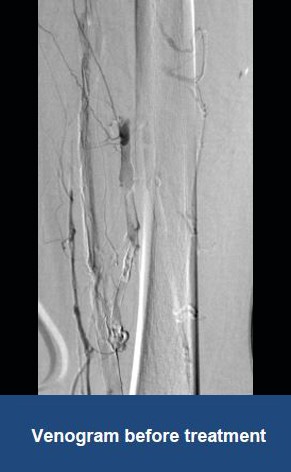
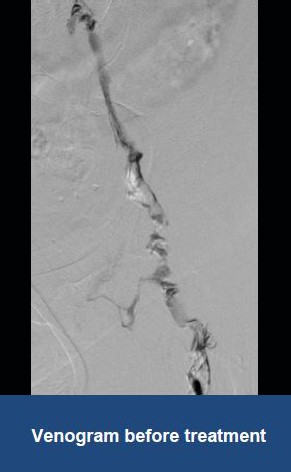
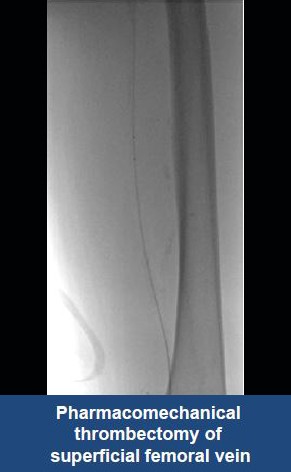
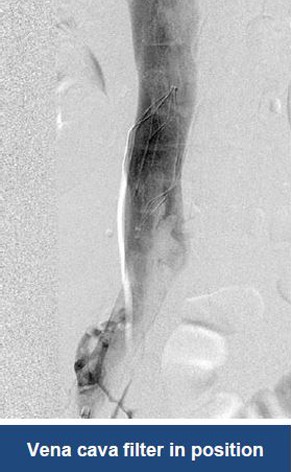
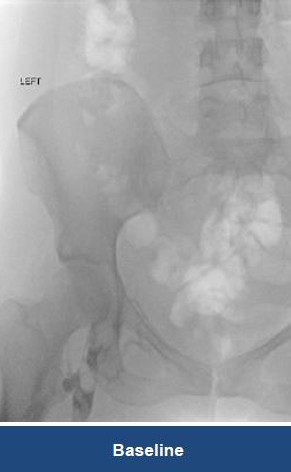
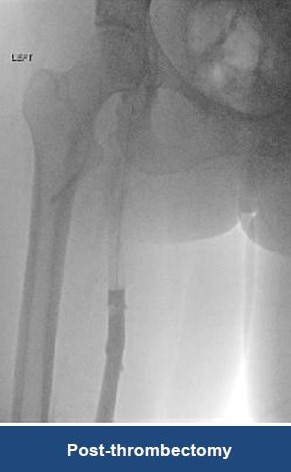
Thrombectomy of Massive DVT

Thrombectomy of Bilateral DVT
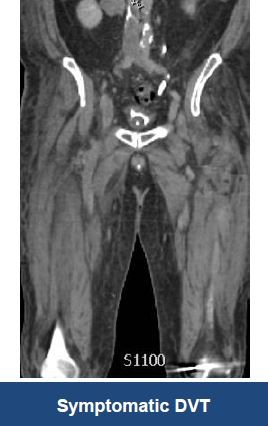
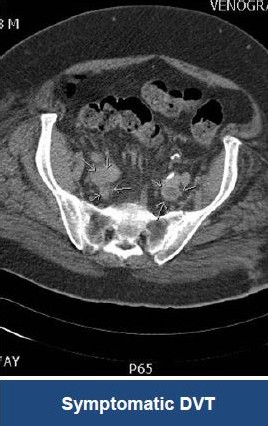
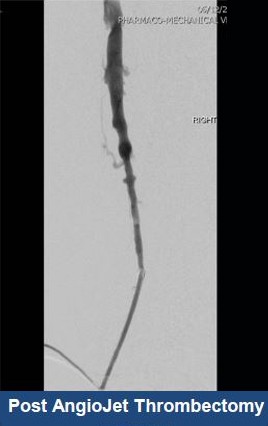
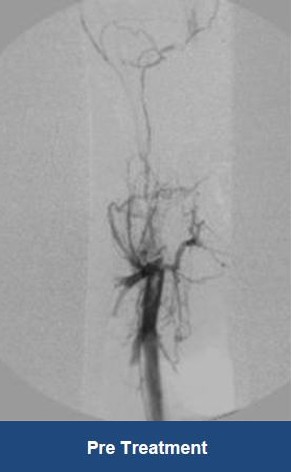
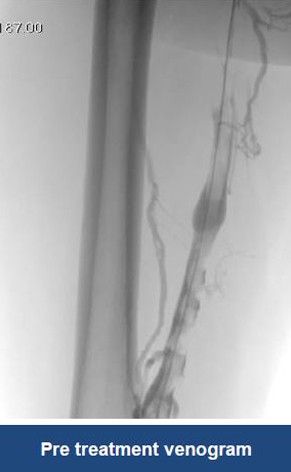
Thrombectomy of DVT
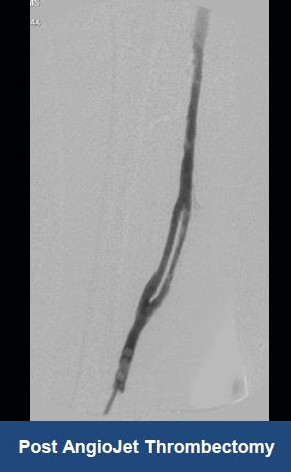
Thrombectomy of DVT
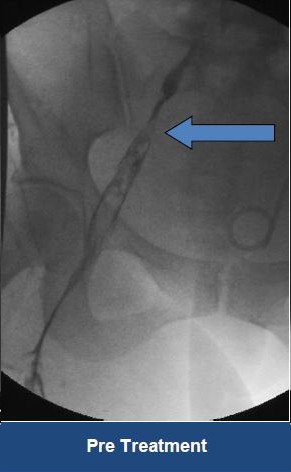
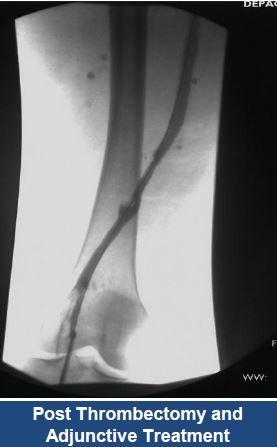
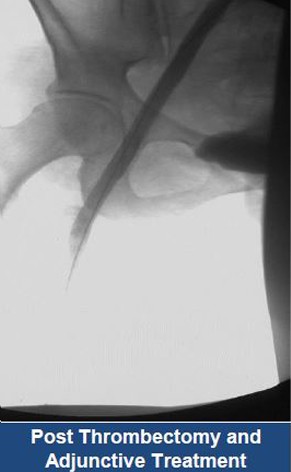
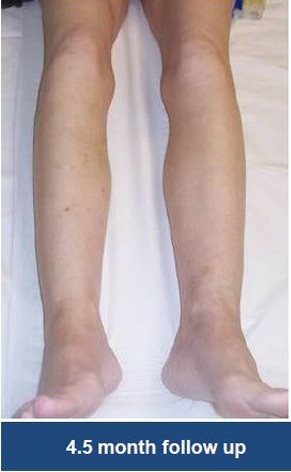
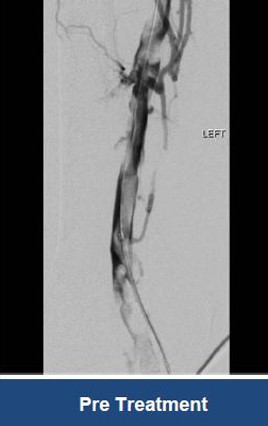
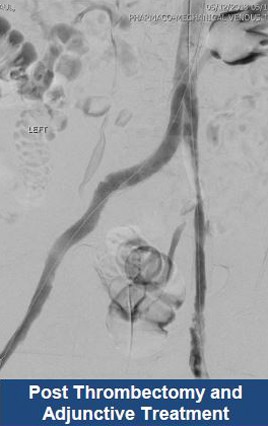
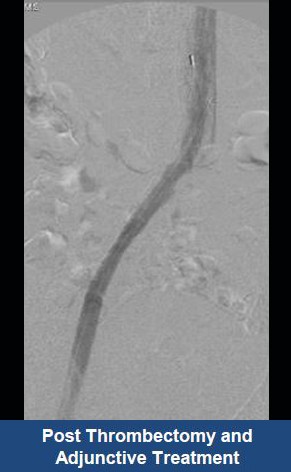
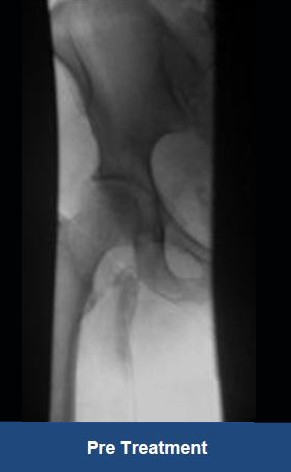
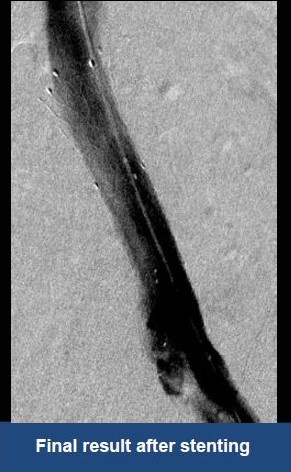
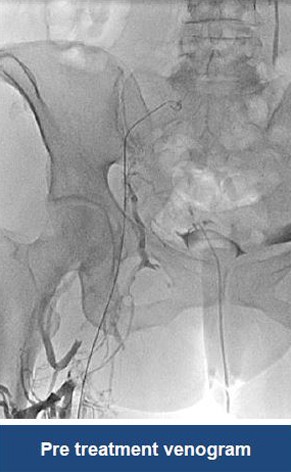
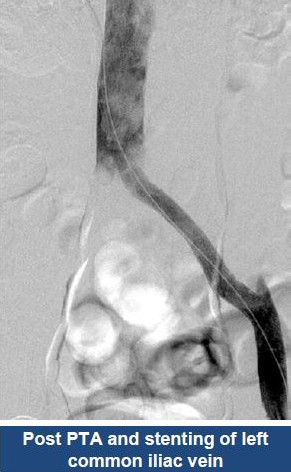
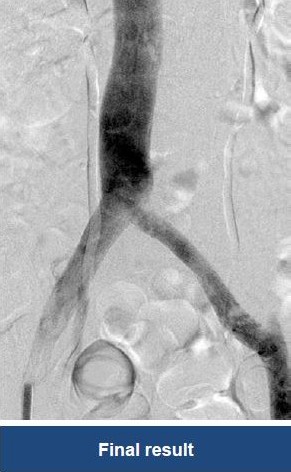
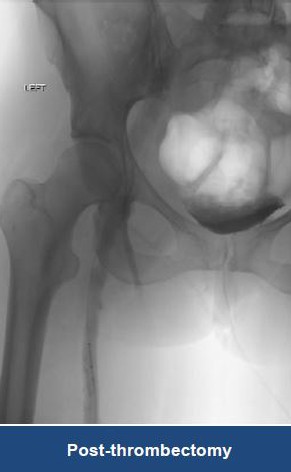
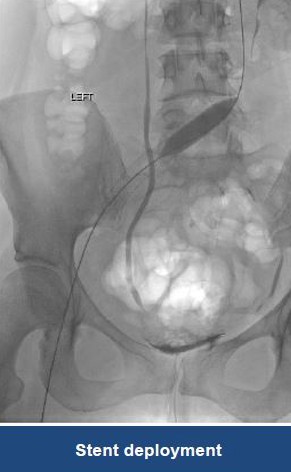
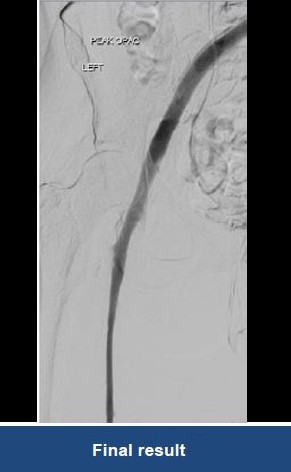
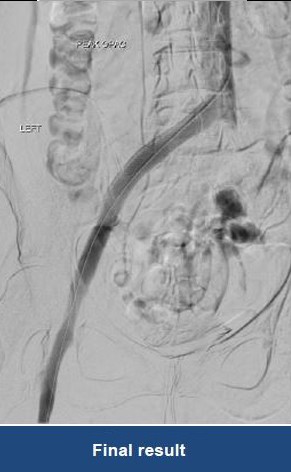
Thrombectomy of Massive Iliofemoral DVT and Stenting for May-Thurner Syndrome
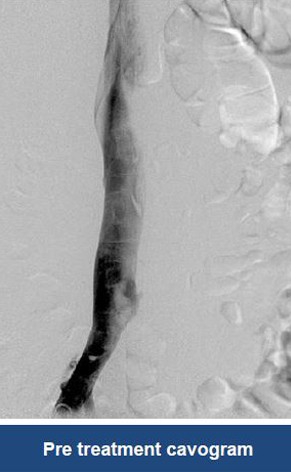
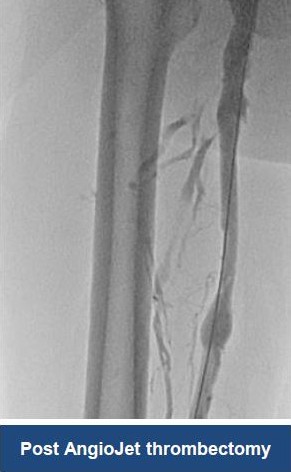
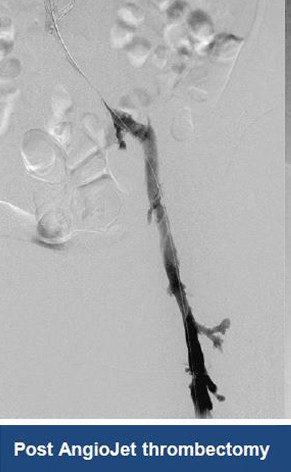
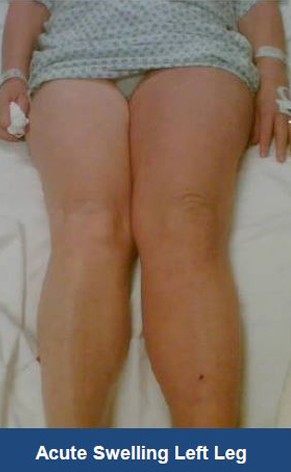
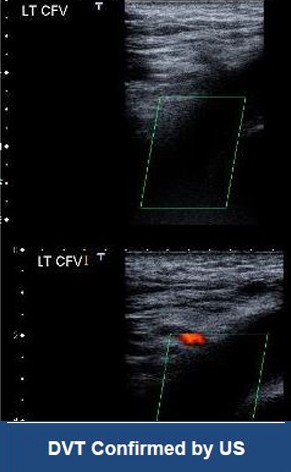
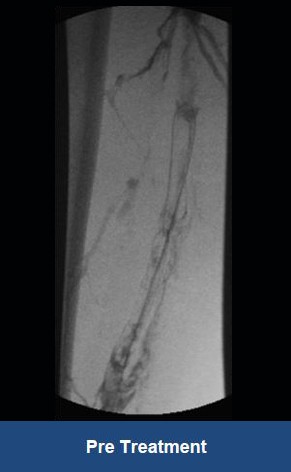
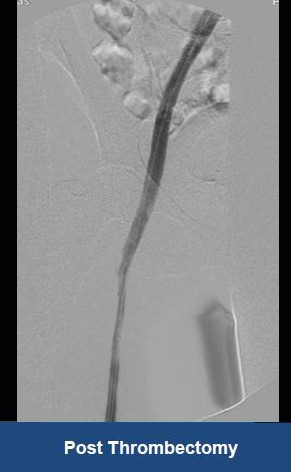
Acute Left leg Ilio femoral DVT managed with AngioJet™ Thrombectomy System and Wallstent Uni™ endoprothesis