What Is Atrial Fibrillation?
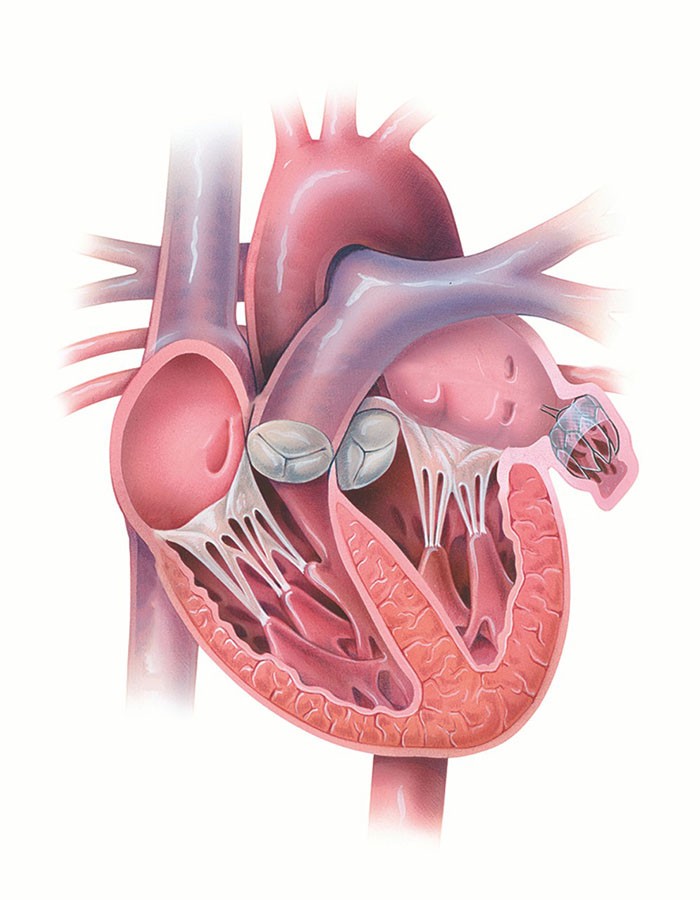
In a healthy beating heart, your blood pumps in a steady, coordinated fashion in the chambers of your heart to and from other parts of your body. Atrial fibrillation (AFib) happens when the top two chambers of the heart, the atria, beat too fast and with an irregular rhythm (fibrillation).
With each beat of your heart, blood is pumped to and from other parts of your body. Your heart’s electrical system controls the pumping. In a healthy heart, the rhythm is steady and coordinated. If you have AFib, the electrical signals are disorganized, causing your atria to quiver rapidly and irregularly (fibrillation) instead of beating in a regular rhythm.1

AFib can decrease the heart’s pumping efficiency by as much as 30 percent. This can cause blood cells to pool and stick together, forming clots in an area of the heart called the left atrial appendage (LAA).
Everyone has a left atrial appendage. It’s about the size of your thumb and looks like a small pouch on the top of your heart. If a clot escapes from the LAA and gets into your arteries, it may block the blood supply to the brain and cause a stroke.
What Is a Stroke?
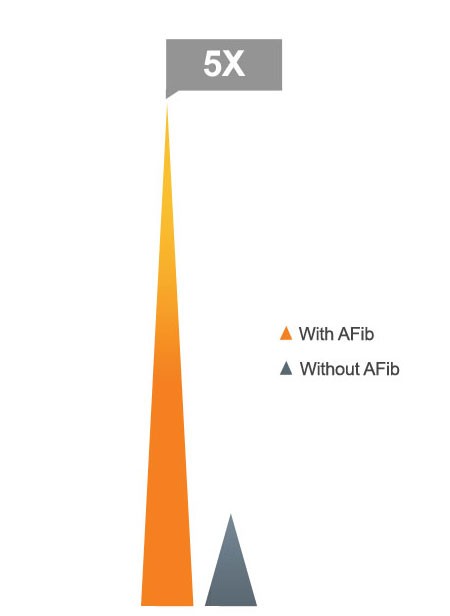
The Connection Between AFIB and Stroke
People with atrial fibrillation have five times the risk of stroke than those with normal heart rhythms.
To understand how AFib causes strokes, it helps to understand how your heart works. Your heart’s electrical system controls the rate and rhythm of your heartbeat. In a healthy heart, the electrical signals produce a steady heartbeat, causing your heart to contract and pump blood. With AFib, the electrical signals are disorganized, causing your atria to quiver (fibrillate) instead of beating in a regular rhythm. As a result, your atria don’t pump blood efficiently, which can cause the blood to pool and form clots that can lead to a stroke.5

Read about the treatment options
for Atrial Fibrillation