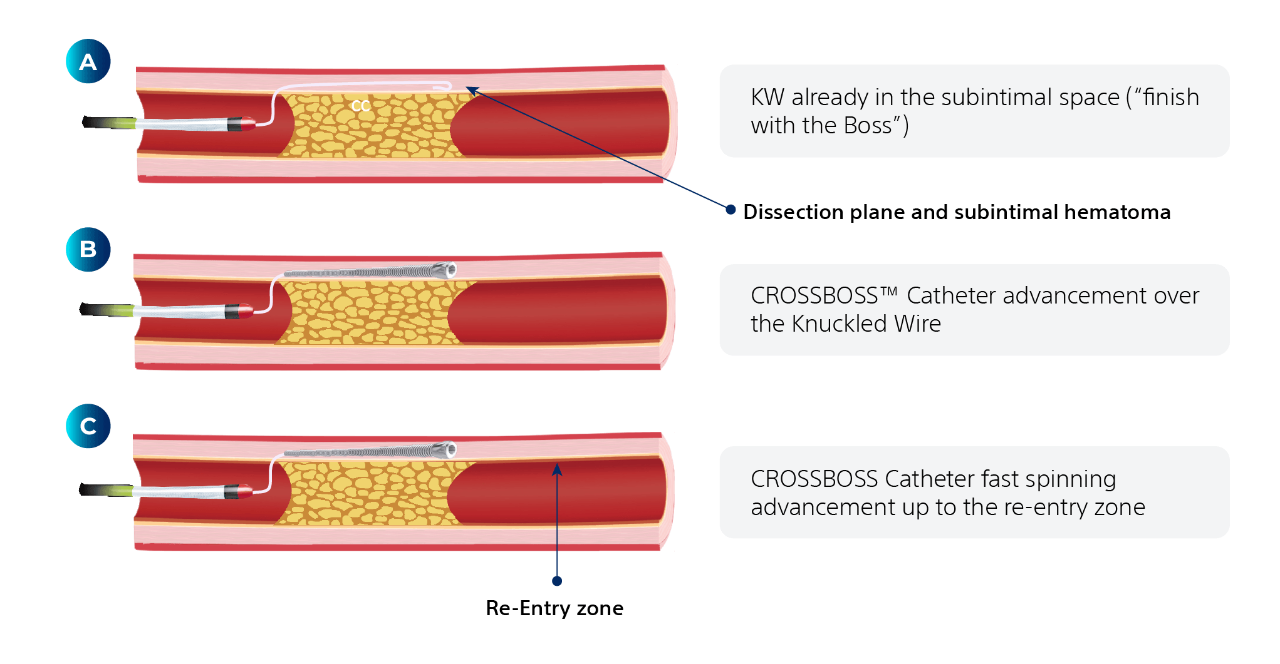
CONTRAINDICATIONS: Do not use with guidewire extension systems with a coupling profile larger than 0.014 in (0.36 mm) diameter (i.e. wave pattern coupling mechanism).WARNINGS: Only physicians thoroughly trained in interventional procedures should use the CrossBoss Catheter. To reduce the potential for vessel damage, the CrossBoss Catheter should only be used in vessels that are ≥1 mm in diameter. Always use the included torque device during catheter advancement and manipulation especially during device rotation. Failure to use the included torque device may result in catheter failure and may result in patient injury.PRECAUTIONS: In coronary applications, the CrossBoss Catheter should only be used in hospitals where emergency coronary bypass surgery can be immediately performed in the event of a potentially injurious or life-threatening complication. Before insertion of the CrossBoss Catheter, administer appropriate anticoagulant and vasodilator therapy. The CrossBoss Catheter should be handled with care. Prior to use and during the procedure, inspect the packaging and catheter for bends, kinks, or other damage. Discontinue use if the catheter becomes damaged. Do not expose to organic solvents. The CrossBoss Catheter should only be manipulated under fluoroscopic observation. Do not use a syringe smaller than 5 cc (ml) when flushing the catheter. Do not use an inflation or power assist device when flushing the catheter.ADVERSE EVENTS: Potential adverse events include, but are not limited to, the following: Acute myocardial infarction, Vessel trauma requiring surgical repair or intervention, Hemorrhage or hematoma, Artery spasm, Embolism, Stroke, Neurological deficit, Drug, reactions, allergic reaction to contrast media, Infection, Recurrence of angina, Chest discomfort, Bleeding from the catheter insertion point, Bruising at the catheter insertion point, Ischemia due to restenosis of the dilated segment, Ventricular failure, Dissection or thrombosis with vessel occlusion, Arterial Perforation (Surgery required), Blood Toxicity, Toxicological response, Fever, Infection at skin puncture site, Deterioration of kidney function/kidney failure, Provocation of heart attack/stroke, Surgery to recover failed devices, Surgery to repair a failed procedure, Prolonged procedure time, Occlusion of a branch of coronary artery, Myocardial infarction with release of CK-MB into circulation, Death, When failures of PTCA occur, they are often treated using coronary artery bypass surgery