Clinical Results
RANGER II SFA Pivotal Trial1
Prospective, Multi-Center, Randomized Controlled Trial Ranger Drug-Coated Balloon vs. Uncoated Balloon (3:1). Follow-up through 5-Years.
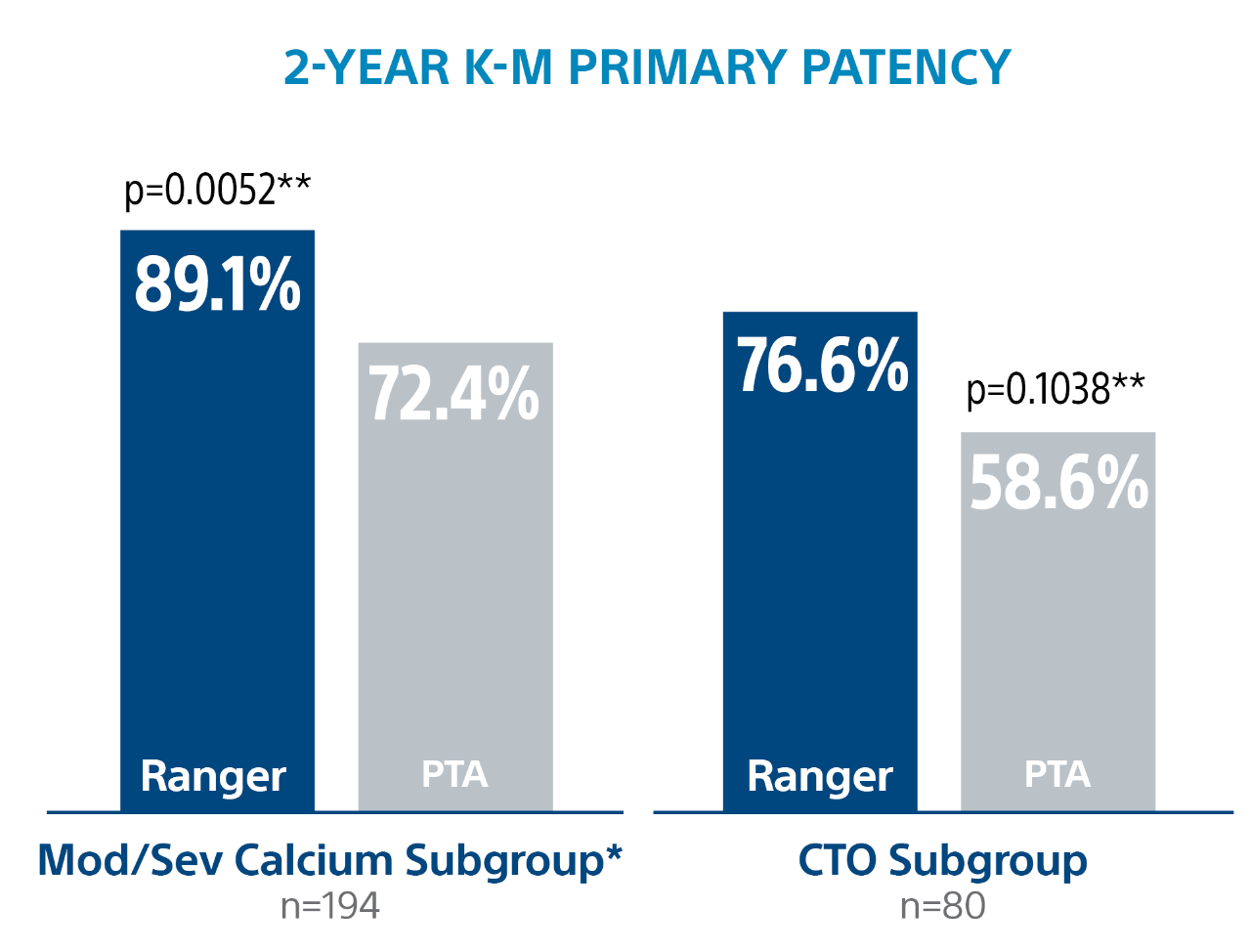
Ranger DCB demonstrated exceptional outcomes at 2-Years. No matter the lesion complexity. No matter the patient1.
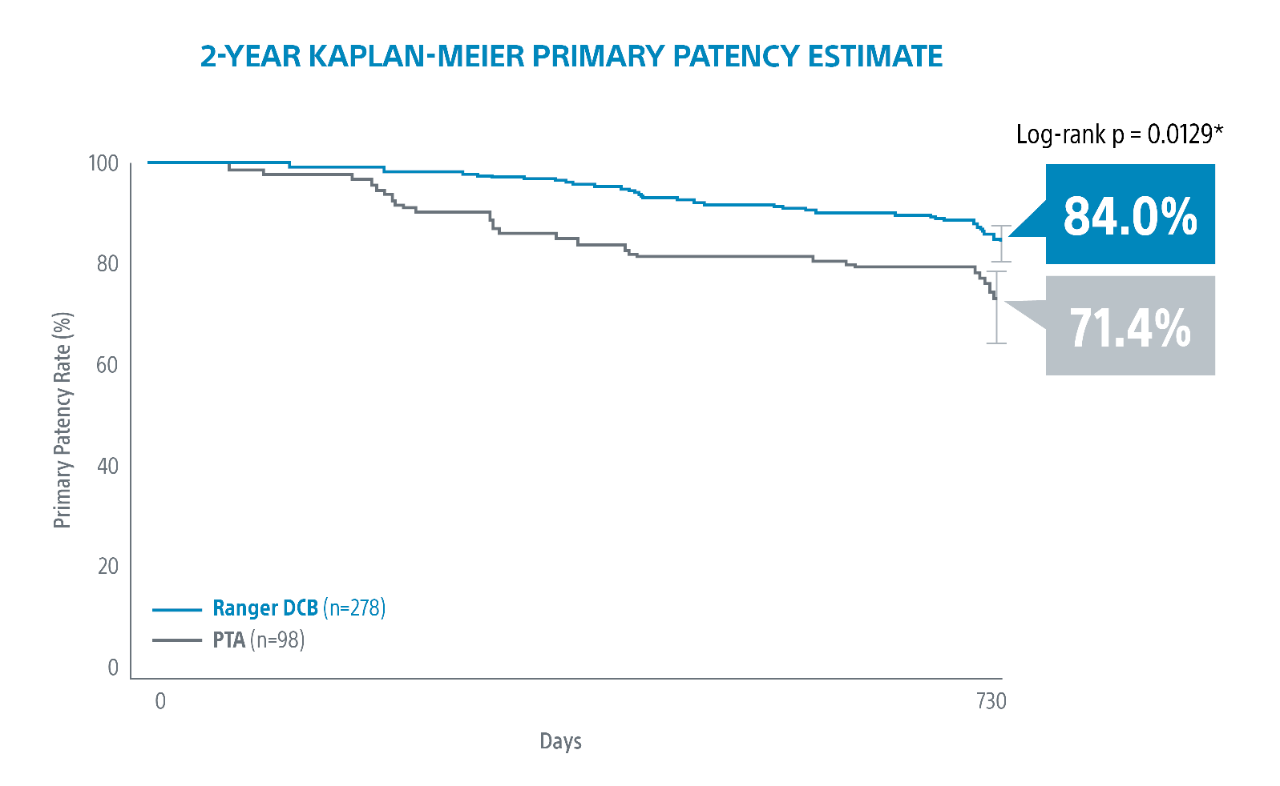
1. RANGER II SFA RCT 2-Year Results presented by Ravish Sachar, MD. VIVA 2021.
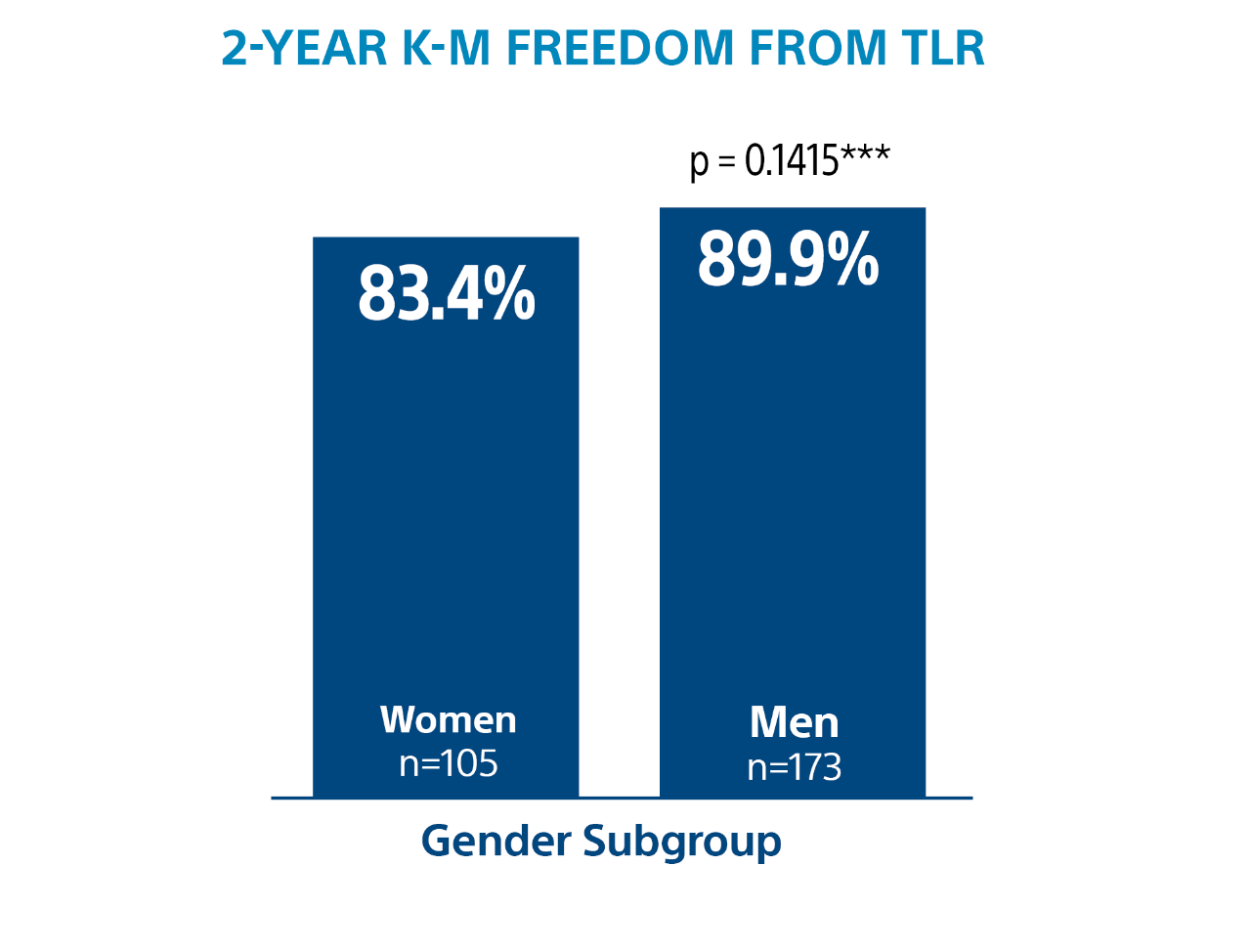
2-Year Subgroup Analysis
** Log-rank p-value compares the entire K-M curves from time point zero to day 760 (full 2-year follow-up window)
*** Log-rank p-value compares the entire K-M curves from time point zero to day 730 (full 2-year annual visit mark)
RANGER II SFA PK Sub Study1

Ranger II SFA Pivotal Trial Details
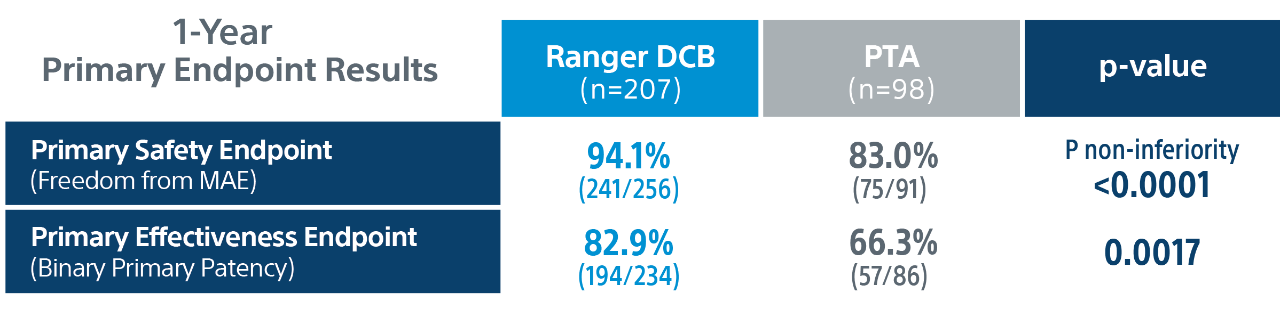
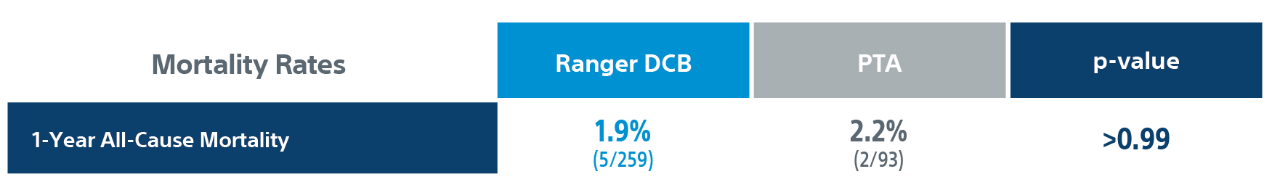
** Core lab.
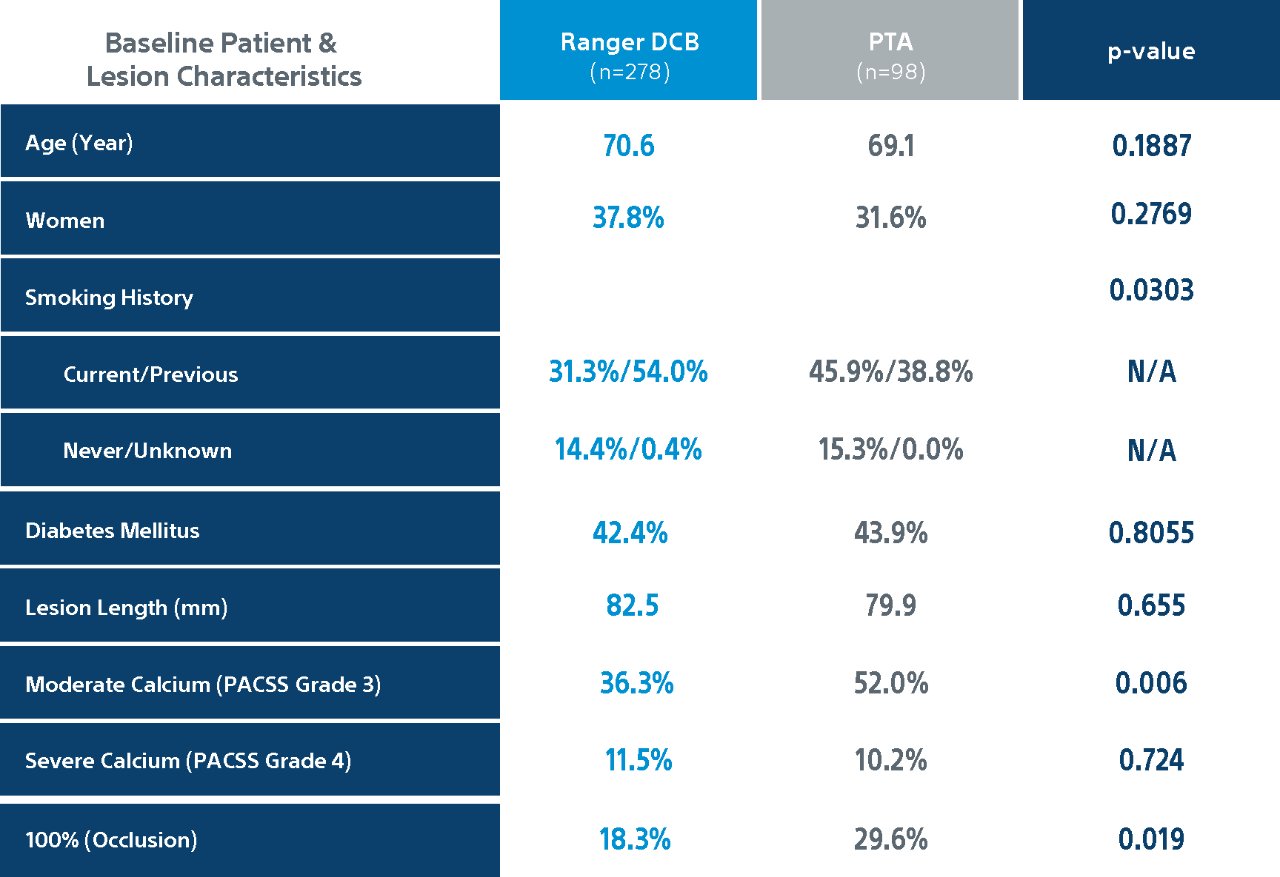
*** PACSS Grade 3/4 may be considered similar to moderate/severe calcification. Grade 3: 36.6% Ranger DCB, 52.0% PTA, p=0.006, Grade 4: 11.5% Ranger DCB, 10.2%% PTA, p=0.724.
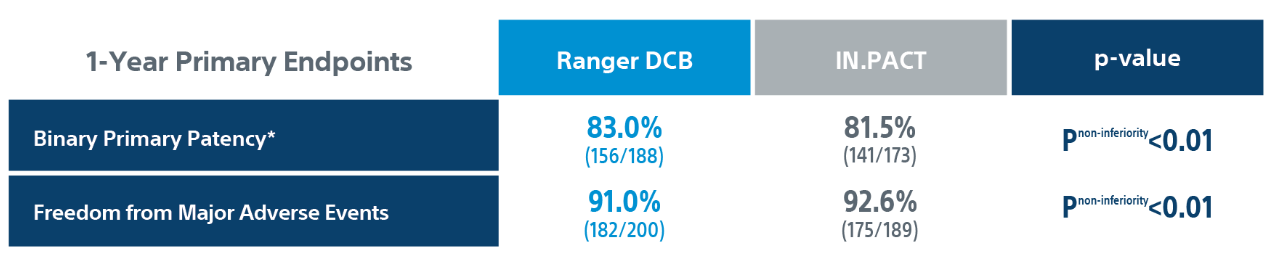
COMPARE Randomized Controlled Trial Results1
COMPARE is the World’s First Head-to-Head Prospective, RCT (1:1) directly comparing SFA DCBs – low dose Ranger DCB vs higher dose IN.PACT DCB.
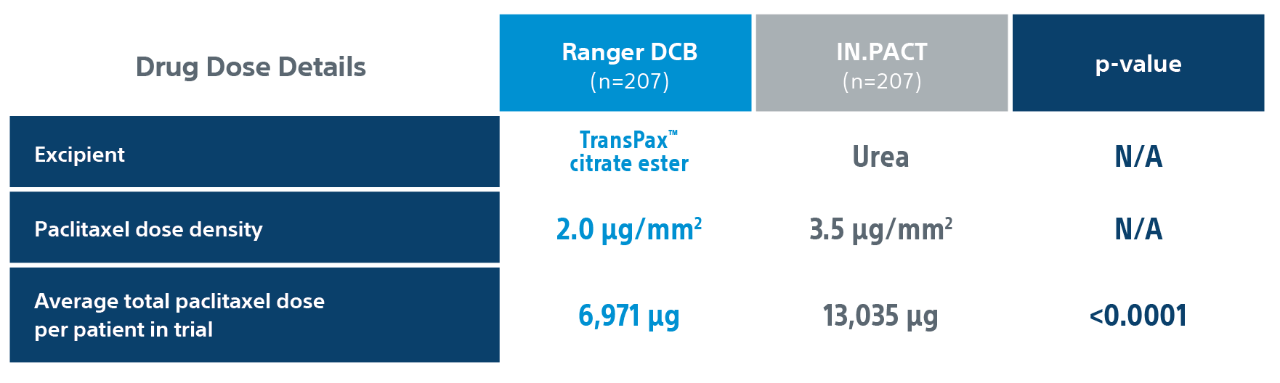
Ranger DCB demonstrated similar primary patency as IN.PACT at 2-Years1 with half the total drug dose2.
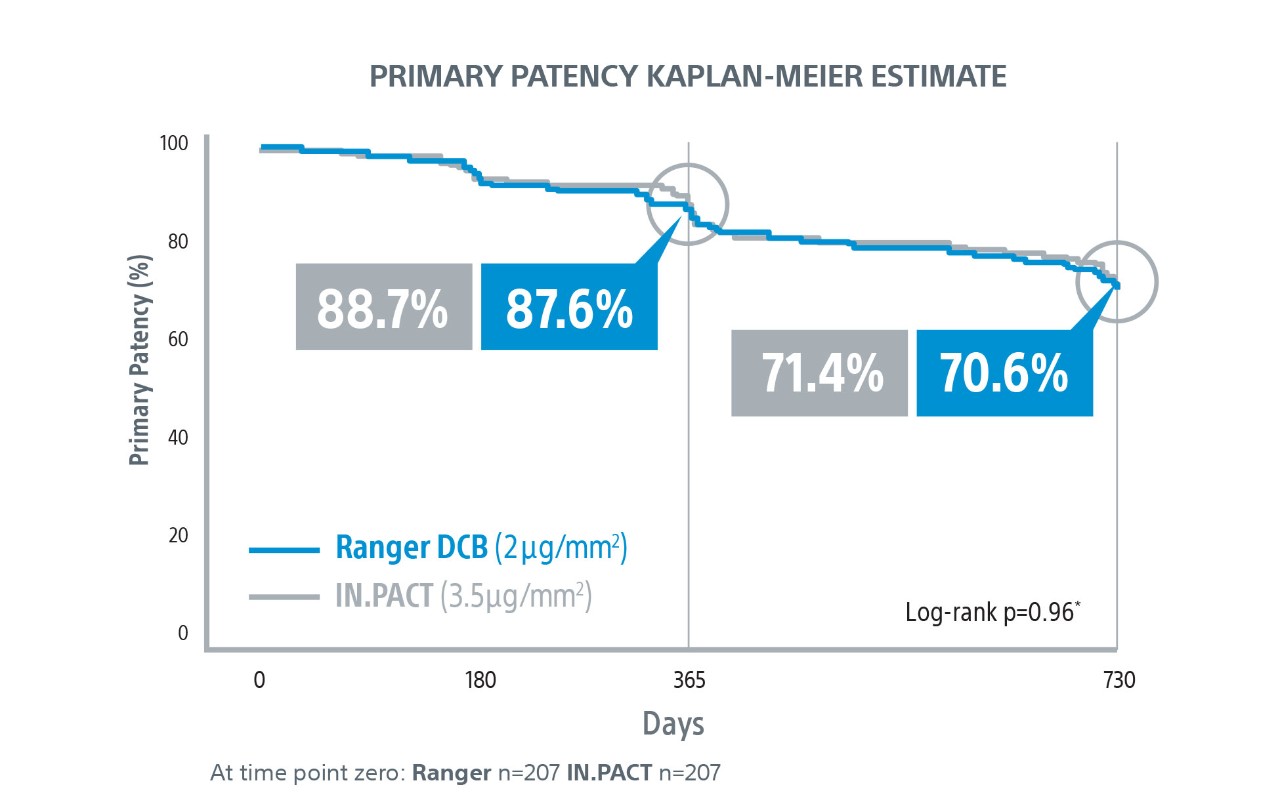
1. COMPARE Clinical Trial 2-Year Results presented by Sabine Steiner, MD. LINC 2021.
2. Based on total drug dose for (4mmx60mm) or (averages for full size matrix) per the Ranger™ Paclitaxel-Coated PTA Balloon Catheter and IN.PACT™ Admiral Instructions for Use.
COMPARE Randomized Controlled Trial Details
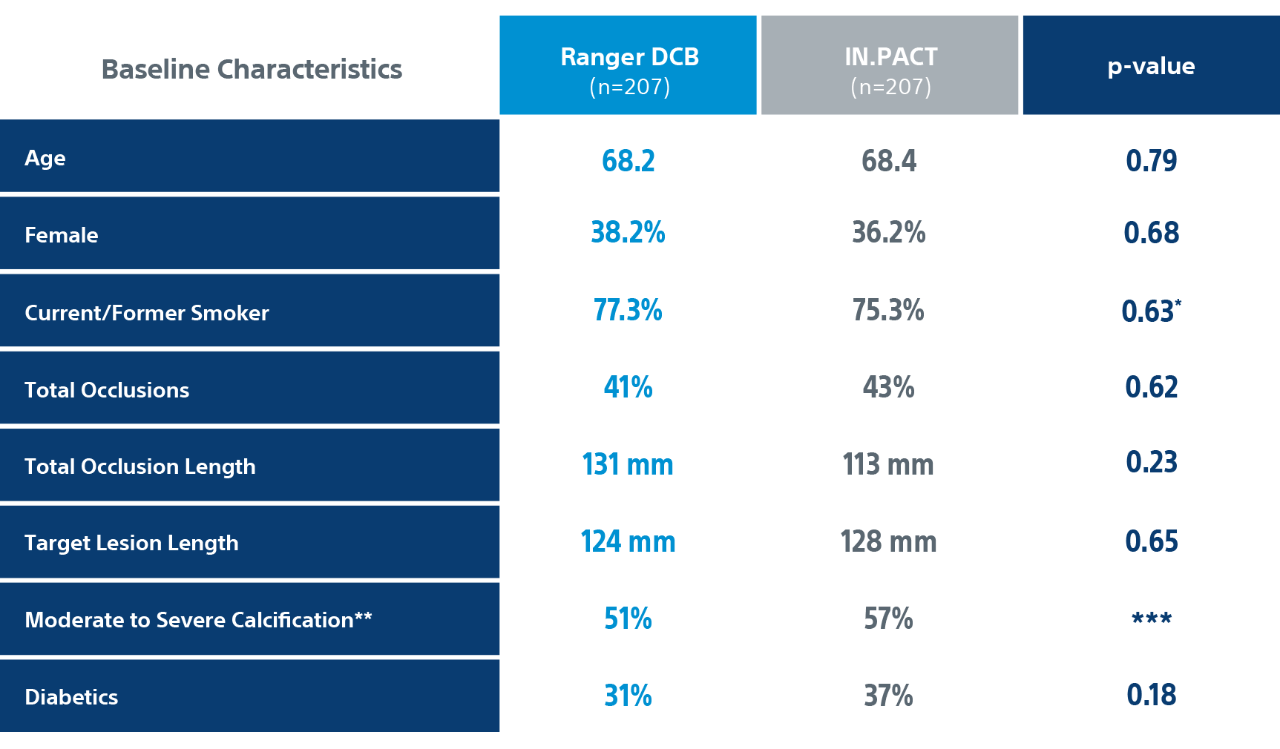
** PACSS Grade 3/4 may be considered similar to moderate/severe calcification.
*** p-value for entire distribution of PACSS Calcium Grades 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 calcium for RANGER DCB vs IN.PACT p-value was 0.20.
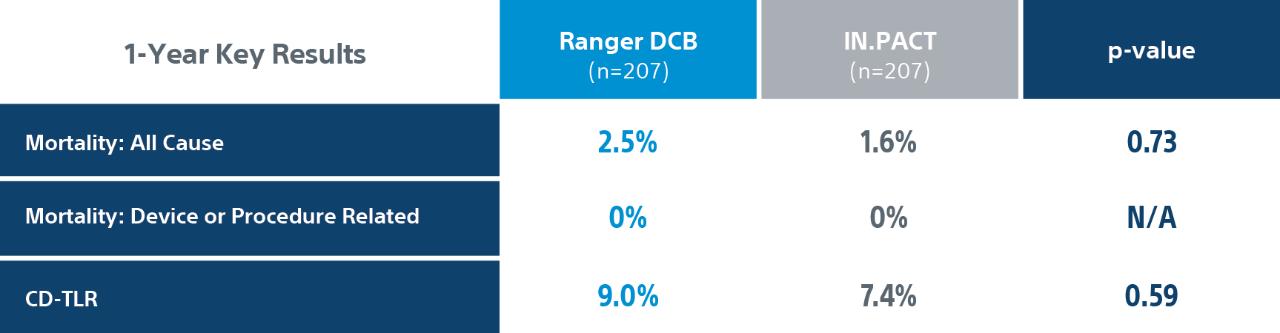
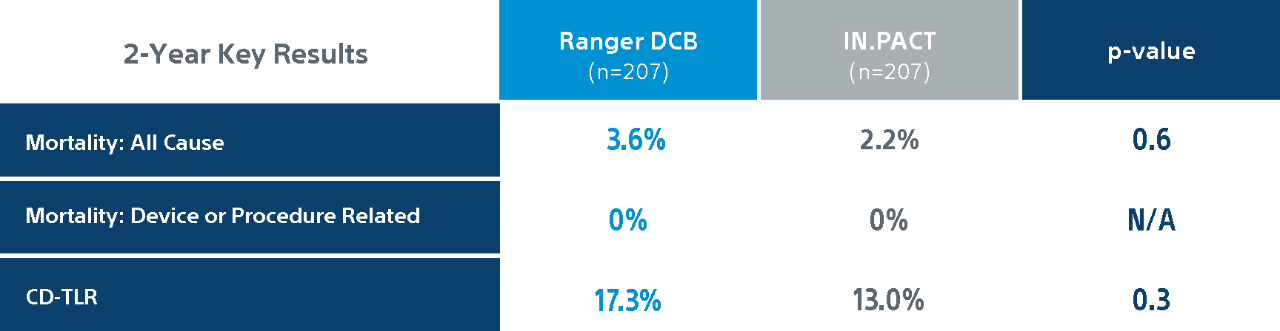
Primary efficacy endpoint: primary patency at 1-Year defined as absence of clinically driven target lesion revascularization (CD-TLR) or binary restenosis determined as a peak systolic velocity ratio > 2.4 evaluated by duplex ultrasound core laboratory analysis.
CD-TLR: a reintervention performed for ≥ 50% diameter stenosis (confirmed by angiography) within ± 5 mm proximal and/or distal to the target lesion after documentation of recurrent clinical symptoms of PAD (increase of 1 Rutherford class or more) and/or drop of ABI (≥20% or >0.15 when compared to maximum early post-procedural level).
Explore DE Resources
Get physician perspectives, clinical data sheets and other resources about drug-eluting innovations.
Stay Up to Date
Receive emails about the latest drug-eluting technology news, innovations and events in your area.